A tech stack, or technology stack, is a collection of tools, frameworks, and programming languages developers use to create software. The tech stack you choose doesn’t just affect how quickly you can develop; it also plays a key role in how scalable, maintainable, and high-performing your product will be in the long run.
In this article, we will take a closer look at what is a tech stack, review some of the most popular technologies today, and help you select the best one for your project.
1. What is a tech stack?

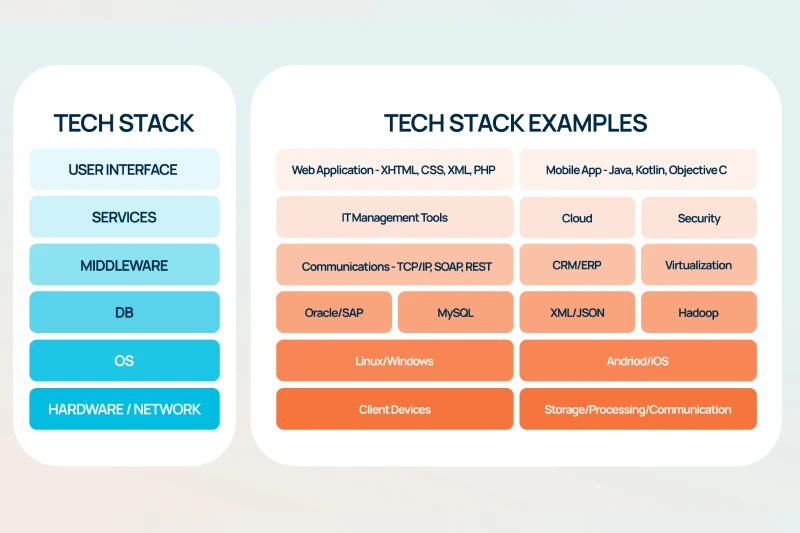
A tech stack is a collection of technologies that create a software product. Imagine it as a multi-layered cake, where each layer ensures the application runs seamlessly. Let’s break down the key components of a tech stack:
1.1. Front-end (User Interface)
This program section’s design and user experience are directly interacted with by users. Among the popular technologies are:
- HTML & CSS: Define the structure and styling of web pages.
- JavaScript: Gives webpages dynamic behavior and interactivity.
- Popular frameworks: React, Angular, and Vue streamline development and optimize front-end performance.
1.2. Back-end (server-side processing)
The back-end is about connecting to databases, handling data, and running business logic. Here are some of the essential technologies that come into play:
- Check out programming languages, including Python, Ruby, Java, and Node.js.
- Popular frameworks include Express.js for Node.js, Django for Python, and Ruby on Rails for Ruby. These frameworks help organize code and boost development efficiency.
- APIs, or Application Programming interfaces, bridge the front-end and back-end, allowing for smooth communication.
1.3. Database

The database stores and manages information, ensuring smooth application functionality. Some popular database management systems include:
- Relational databases (SQL): The best options for applications using well-structured data are MySQL and PostgreSQL.
- NoSQL databases: MongoDB – More flexible, ideal for handling unstructured data like social media content.
1.4. Server & Operating system
This is where the application is hosted, processed, and operated, including:
- Server operating systems: Linux, Windows.
- Cloud hosting services like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud provide fantastic scalability, top-notch security, and a dependable infrastructure for your applications.
1.5. APIs serve as the connection between the front-end and back-end
An API, or Application Programming Interface, acts like a bridge allowing different parts of an application to communicate. For example, in e-commerce, when you place an order through an app, the API quickly transfers data from the user interface to the server, kicking off the transaction process.
To build a high-quality application, it’s essential to understand what a tech stack is and how various technologies work together. Choosing the right tech stack ensures your project runs smoothly, remains easy to maintain, and can scale as needed over time.
Looking for a Tech Partner Who Delivers Real Results?
We provide tailored IT solutions designed to fuel your success. Let`s map out a winning strategy. Starting with a free consultation.
Connect with an ExpertRead more >>> 8 Types of Software Development in 2025: A Comprehensive Guide
2. Popular tech stacks in modern development
Every web development project has unique requirements, and choosing the right tech stack can significantly impact performance, scalability, and maintainability. Below are some of the most popular tech stacks in modern software development.
2.1. MEAN Stack

The full-stack JavaScript-based tech stack MEAN simplifies front-end and back-end development using a single language.
- Components: MongoDB (database), Angular (front-end framework), Express.js (back-end framework), and Node.js (runtime environment).
- Advantages: Highly scalable; perfect for dynamic online applications; fully JavaScript-based, facilitating more seamless and unified development.
- Use cases: Dynamic web platforms, e-commerce systems, and real-time applications.
2.2. MERN Stack

MERN is quite similar to MEAN, but it swaps out Angular for React, giving you a more flexible and contemporary front-end experience.
- Components: MongoDB, Express.js, React.js, Node.js.
- Advantages: React’s component-based architecture makes it a breeze to develop user interfaces and keeps maintenance simple.
- Use cases: Single-page applications (SPAs), e-commerce platforms, and management dashboards.
2.3. LAMP Stack

LAMP is a traditional and time-tested tech stack that remains popular due to its stability and cost-effectiveness.
- Components: Linux (operating system), Apache (web server), MySQL (database), PHP (programming language).
- Advantages: Widely supported, cost-efficient, and versatile for various applications.
- Use cases: Content management systems (CMS) like WordPress, traditional websites, and blogs.
2.4. JAMstack

JAMstack is an innovative web architecture emphasizing speed, security, and easy deployment.
- Components: JavaScript (which powers the interactivity of applications), API (responsible for data communication), and Markup (static HTML files).
- Advantages: It offers high performance, improved security, and straightforward scalability.
- Use cases: This is the most suitable for static websites, blogs, and e-commerce storefronts.
2.5. Other modern tech stacks
Regarding tech stacks, there’s a whole world beyond the popular ones we often hear about. There are plenty of other combinations out there, each designed to meet the unique needs of different projects.
- Vue.js + Firebase: Ideal for lightweight, flexible web applications.
- Python + Django: Great for high-security, data-intensive applications.
- Ruby on Rails is great for quick development, making it an excellent choice for startups looking to get off the ground quickly.
2.6. The connection between full-stack development and the tech stack
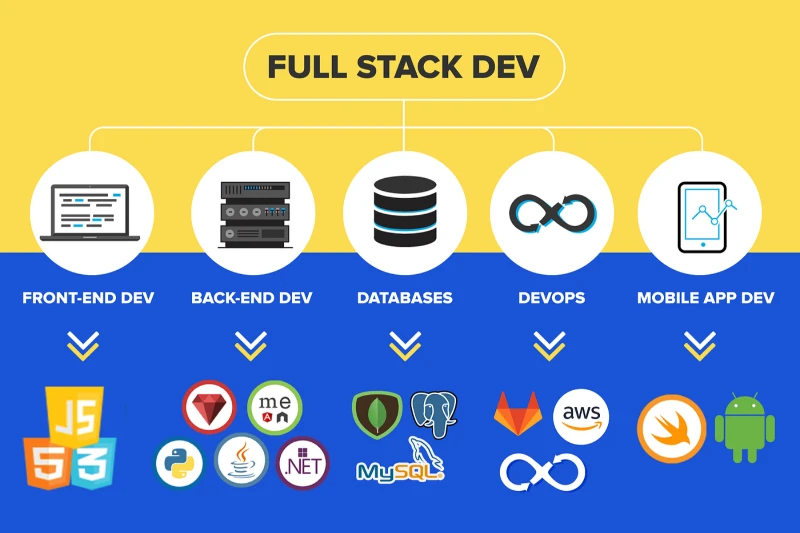
Full-stack development is about creating an application’s front and back end. A full-stack developer juggles various technologies within a tech stack, which empowers them to build a complete product from the user interface to the data processing systems.
To truly shine in full-stack development, it’s essential to grasp what a tech stack is and how its different parts work together. This understanding boosts a developer’s efficiency and helps businesses make smart technology decisions that fit their product strategy. Choosing the right tech stack is key to ensuring smooth development, hassle-free maintenance, and scaling in the long run.
3. Choosing the right tech stack for web development
Choosing the right tech stack can determine the success of a software project. A poor choice can lead to high development costs, maintenance challenges, or scalability issues. Below are key factors to consider when selecting a tech stack for your web project.
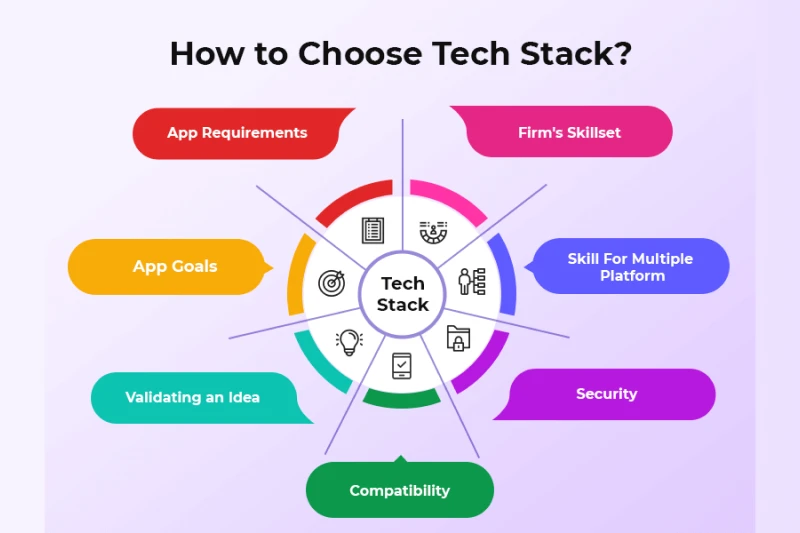
3.1. Project requirements
First, the project scope should be clearly defined. Whether it is a simple personal blog or a complex, large-scale e-commerce platform will matter. Basic requirements like real-time functionality, high-load processing, or security will determine your tech stack decisions. For example:
- JAMstack may better serve a static site.
- MERN or MEAN may be the way for a large-scale SaaS platform.
3.2. Development team expertise
Recognizing all this, it becomes clear that when selecting different technologies for projects, one should know what a tech stack is and how to line it up with your development team’s expertise. For example, if the team consists of JavaScript wizards, a stack may be like MERN or MEAN. With good working experience in Python, a Django-PostgreSQL stack would be a better solution. The right tech stack delivers effortless fury development at maximum value from your developers.
Looking for a Tech Partner Who Delivers Real Results?
We provide tailored IT solutions designed to fuel your success. Let`s map out a winning strategy. Starting with a free consultation.
Connect with an ExpertRead more >>> How to Choose a Software Development Company?
3.3. Scalability
A good system is stable at initial rollout and should also be able to scale with user growth. Ask yourself:
- Can this technology handle millions of users?
- How easy is incorporating new features into the system without causing problems?
- For instance, Node.js is favored for real-time data processing applications, while Go and Rust are great for high-performance systems.
3.4. Community support & Documentation
A tech stack with a strong community makes it easier to find support when you encounter issues. Technologies with extensive documentation and active forums, such as React, Django, and Laravel, are often safer since you can quickly find solutions to common errors.
3.5. Development & Operational costs
Your tech stack impacts not only the initial development cost but also long-term maintenance and operational expenses. Key factors to consider include:
- Programming language: PHP and Python are often more cost-effective due to widespread support from affordable hosting providers.
- Hosting services: AWS and Google Cloud offer powerful but expensive solutions; Heroku or Vercel may be more suitable for smaller projects.
Maintenance Price-Technologies whose interfaces change as often as their underlying frameworks may require some maintenance, greatly escalating total costs.
3.6. Time to market

Pick a tech stack with many pre-built libraries and frameworks if you need to start rapidly. When paired with React and Next, Ruby on Rails and Django are excellent choices for quick MVP development. For projects aimed at SEO optimization, JavaScript is an even better choice.
3.7. Security
Security is crucial when considering a tech stack, especially for sensitive data applications. Some technologies come with built-in security features. For example, Django includes various built-in defenses against CSRF but requires the implementation of security measures by hand for many other frameworks. Therefore, selecting a tech stack would enhance the security and robustness of your application against potential threats.
3.8. Aligning with business goals
Choosing a tech stack is not just a technical choice; it should be in tune with your business objectives. If you are creating a SaaS product, you want to choose tech that supports subscription models and scales easily. For the e-commerce platform, choose technologies that facilitate quick and safe transactions that can handle volumes during heavy traffic. A good tech stack aligns with the technical and business needs the product should fulfill.
3.9. Modern tech stack trends in 2025

Technology never ceases to progress. Indeed, some of the newer advancements and innovations in technology dictate the choice of tech stack in its entirety. Here are some of the key tech stack trends that every person will be watching in 2025:
- Serverless architecture: Reduce operation costs while improving scalability and eliminating needing a physical server to manage.
- Edge computing: Processes the data closer to the users to provide faster processing and lower latency performance.
- AI-powered development tools: Embedding AI into development processes for improved productivity and repetitions getting automated.
- Low-code/No-code platforms: Enable businesses to deploy applications quickly without a big development team.
It will not simply be a technical decision, but rather, it will influence the long-term fate of your project. Before selecting a tech stack, one should carefully weigh project needs, team talent, cost, security, and scalability. A properly chosen kit lets your product remain stable, maintainable, and scalable amidst the winds of change that blow across the digital landscape.
4. Conclusion
Knowing what is a tech stack means, not just how well it performs or scales; it goes into cost, time for development, and the long-term maintenance of applications. Different apps will have different needs. Thus, every aspect of business objectives, available team skills, operational costs, and changing trends in technology should be carefully considered before making a choice.