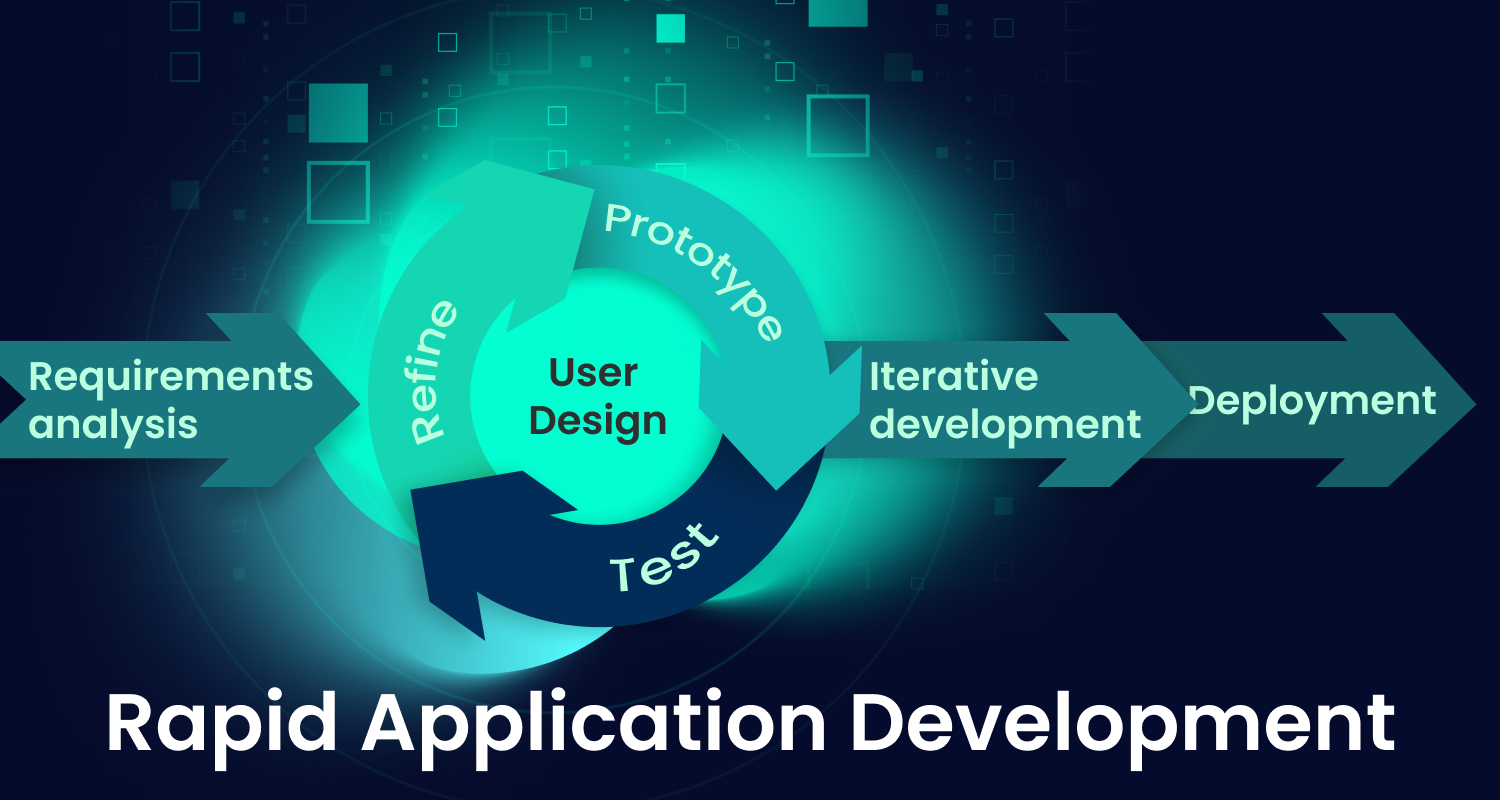
The rapid application development model is a software development methodology focusing on speed and flexibility. It uses iterative development and software prototyping to quickly create working applications with user feedback at each step.
1. What is rapid application development?
The rapid application development model is a software development methodology designed for speed and flexibility. It allows teams to build software quickly using prototypes, ongoing user feedback, and fast iterations. Instead of following a strict plan, RAD encourages developers to adjust as they go, making it ideal for projects where requirements are expected to change.
James Martin first introduced the RAD model in the 1980s. He wanted to create a method to shorten development cycles while delivering quality software. Around the same time, Barry Boehm also influenced the evolution of iterative and adaptive models through his work on the Spiral model. Their combined ideas helped shape modern development teams’ thinking about speed, user involvement, and flexibility.
2. 4 Phases of RAD
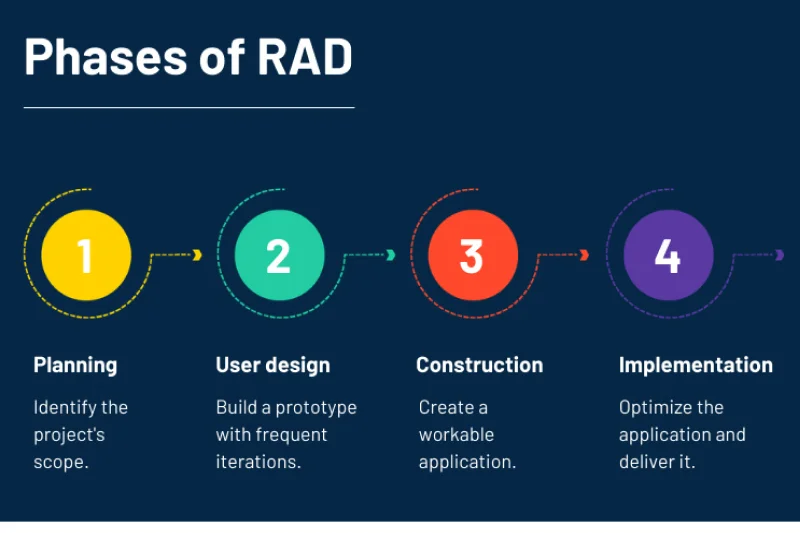
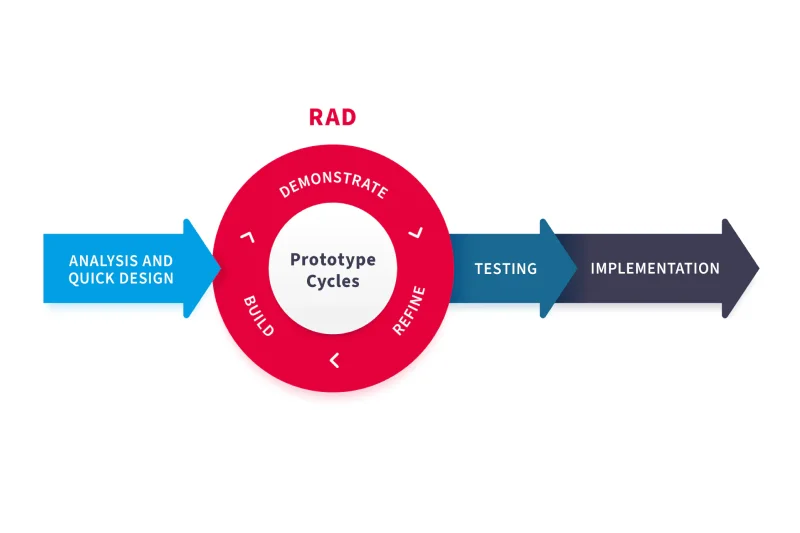
The RAD model is divided into four main phases. Each phase supports speed, flexibility, and active user involvement. These steps help teams deliver working software faster, using RAD development phases and tools focusing on efficiency and collaboration.
Read more >>> V-Model in Software Development: Process, Advantages, and Best Practices
2.1. Requirements planning phase
In this first step, developers and stakeholders define the project goals. They identify business needs, user expectations, and technical requirements. Unlike traditional models, this phase is quick and focused. The goal is to create a shared understanding of what needs to be built—without spending too much time on long documents.
2.2. User design phase
This phase is all about software prototyping techniques. Developers and users work side by side to create mockups and early application versions. Feedback is gathered in real-time, which helps shape the design. It’s a back-and-forth process where ideas are tested, improved, and refined until users are satisfied with the interface and functionality.
2.3. Construction phase
Once the design is approved, the real coding begins. This phase uses iterative development, meaning the product is built in small parts, tested, and improved continuously. Developers use feedback from earlier prototypes to shape the final system. Because the foundation is already set, coding and testing happen quickly and efficiently.
2.4. Cutover phase
In the final stage, the finished application is launched. This includes data migration, final testing, user training, and deployment. Teams ensure a smooth transition from the old system to the new one.
Throughout all these phases, RAD development phases and tools like low-code platforms and visual builders help speed up the process. These tools support rapid changes, reduce manual coding, and improve collaboration between developers and users.
Following this structure, the rapid application development model allows teams to deliver high-quality software in less time, with better alignment to user needs.
Want to Integrate Powerful IT Solutions into Your Business?
We provide tailored IT solutions designed to fuel your success. Let`s map out a winning strategy. Starting with a free consultation.
Contact UsRead more >>> Exploring Nearshore Agile Development: Benefits and Best Practices
3. RAD tools
To support the rapid application development model, developers rely on various tools that speed up designing, building, and delivering software. These tools are designed to reduce manual work and allow quick updates based on user feedback.
One of the most popular categories is low-code development platforms. These platforms let developers create applications with minimal hand-coding. Instead of writing every line of code, they use drag-and-drop features, visual builders, and pre-built components. This makes building and adjusting prototypes quickly during the design phase easier.
Other useful tools for rapid application development include:
- Prototyping software: These help create working models of the application early in the process, making it easier to collect feedback and refine the design.
- Collaborative tools: Platforms like shared whiteboards, user feedback apps, and real-time editing tools allow teams and clients to work together closely.
- Testing automation tools: Automated testing speeds up the process of identifying bugs and ensures consistent quality throughout development.
These tools all play a big role in streamlining the RAD process. They reduce the time spent on repetitive tasks, make it easier to adapt to changing needs and help teams deliver working software faster.
With the help of low-code development platforms and other RAD tools, the rapid application development model becomes a practical choice for businesses that value speed, flexibility, and strong user involvement.
4. Advantages and disadvantages of RAD

4.1. Advantages of RAD
The rapid application development model offers several benefits, making it a strong choice for many software projects. It’s especially helpful in fast-moving environments where requirements often change, and quick delivery is essential.
One of the biggest advantages of the RAD model is speed. Development teams can build and release applications much faster than traditional models by using prototypes, frequent testing, and user feedback. This leads to a shorter time-to-market, which is crucial for businesses that must stay competitive.
Another key benefit is enhanced user involvement. In RAD, users are included throughout the process—from planning and design to testing and final delivery. This ensures the end product closely matches what users need and expect.
4.2. Disadvantages of RAD
While the rapid application development model offers many benefits, it also has some downsides that teams should consider before choosing it. Understanding both the advantages and disadvantages of RAD model can help you make the right decision for your project.
One major challenge is scalability. The RAD approach works best for small to medium-sized projects. It can become difficult to manage when applied to large systems with complex requirements. Too many moving parts and constant changes can slow things down instead of speeding them up.
Another issue is the need for highly skilled developers. RAD depends on quick decision-making, effective communication, and the ability to build and modify prototypes quickly. If your team lacks experience or technical skills, the model may not work well.
5. Benefits of RAD in software engineering
One of the biggest benefits is improved software quality. Thanks to iterative testing, issues are found and fixed early. Developers build working prototypes and refine them continuously based on feedback. This process reduces the risk of major errors at the end of the project.
Another key advantage is reduced development costs. Since RAD relies on reusable components, rapid prototyping, and faster cycles, it helps optimize time and resources. Teams can deliver more with fewer delays and avoid long planning phases that may never match real user needs.
The rapid application development model also ensures better alignment with user expectations and business goals. Users are involved from the beginning, and their feedback shapes the direction of the project. This leads to a final product that meets both technical and business requirements more accurately.
6. Drawbacks of RAD

While effective in many scenarios, the rapid application development model also has its downsides. One major issue is reduced scalability. RAD is not always suitable for large, complex systems where structure and detailed planning are essential.
Another challenge is scope creep-the tendency for project features to expand during development. Since RAD supports ongoing changes, projects can easily grow beyond their original goals if not managed carefully.
7. Conclusion
The rapid application development model is a smart choice for teams looking to build software quickly while staying flexible. It uses prototyping, user feedback, and iterative development to deliver high-quality results fast. This model works especially well for projects with changing requirements or tight deadlines.
However, RAD isn’t ideal for every situation. It fits best with small to medium projects and skilled teams. If your project needs constant user input and quick updates, the rapid application development model can be a great solution. Just be sure to manage scope and team resources carefully.