
In today’s fast-moving digital world, businesses need IT solutions that are flexible, scalable, and cost-effective — and that’s where Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) steps in. As one of the core models of cloud computing, IaaS offers a more innovative way to manage servers, storage, and networking without the hassle of owning physical hardware. Whether you’re running a startup or modernizing enterprise systems, understanding IaaS can be a game-changer for how you build and grow in the cloud.
1. What is IaaS?
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a cloud computing model that delivers virtualized computing resources—like, like servers, storage, and networking—over on the Internet. Instead of investing in expensive hardware or managing physical data centers, businesses can rent IT infrastructure from a cloud provider on a pay-as-you-go basis. This model offers the flexibility to scale up or down depending on your needs, making it ideal for growing companies or fluctuating workloads.

To better understand IaaS, it helps to look at it in the context of other cloud computing service models. There are three main models:
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): You manage the applications, data, and operating system while the cloud provider handles the hardware, virtualization, and networking.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service): The provider offers infrastructure and development tools and frameworks so you can build and deploy applications without worrying about the backend.
- SaaS (Software as a Service) is the most hands-off model. Software is delivered fully over the Internet and is ready to use, like Gmail or Microsoft 365.
Each model offers different levels of control, flexibility, and responsibility, but cloud computing infrastructure begins with IaaS—the foundation that powers everything else.
2. How does IaaS work?
At its core, Infrastructure as a Service delivers virtualized computing resources through the cloud. Instead of setting up physical servers or networking equipment on-site, users access these resources via the Internet, just like streaming a movie, but for your entire IT setup.
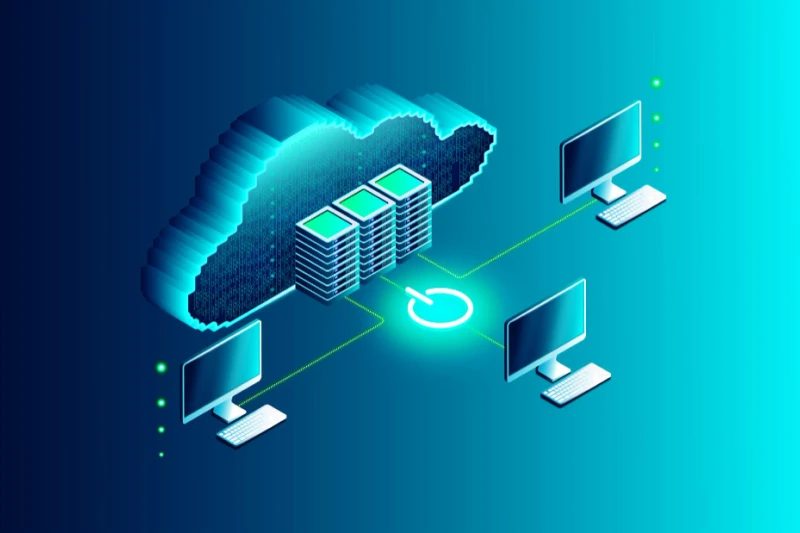

Here’s how it all comes together:
- Virtualized resources: With IaaS, traditional hardware components like servers, storage, and networking are replaced with virtual machines that run on powerful physical servers in remote data centers. These virtual machines (VMs) can be created, configured, and scaled on demand, offering flexibility that physical infrastructure can’t match. Need more processing power for a big launch? Spin up a few extra VMs in minutes.

- The role of data centers and virtualization: IaaS providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform operate massive data centers worldwide. These facilities have top-tier hardware, cooling systems, and security protocols. What makes IaaS possible is virtualization technology—software that slices up physical hardware into multiple isolated environments, allowing multiple users to share the same physical resources without interfering with each other.
- User access through APIs and dashboards: Users interact with the IaaS environment through intuitive dashboards and powerful APIs (Application Programming Interfaces). These tools allow businesses to configure servers, manage storage, and monitor performance without physically touching a piece of hardware. This user-friendly control is a primary reason why cloud computing infrastructure powered by IaaS is becoming the go-to choice for modern IT teams.
3. 3 Types of IaaS
Not all Infrastructure as a Service setups are created equal. Depending on your organization’s needs—security, control, or scalability—you can choose from different types of IaaS: public, private, or hybrid. Each offers unique benefits and trade-offs when managing your cloud computing infrastructure.
3.1. Public IaaS
Public IaaS is the most common model, where cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform, or Microsoft Azure offer shared infrastructure over the Internet. It’s cost-effective and easy to scale, making it an excellent choice for startups, small businesses, or organizations looking for flexibility without managing physical servers.
Benefits:
- Lower upfront costs
- High scalability
- Quick deployment
- Managed by the provider
Considerations:
- Shared resources may raise security concerns for sensitive data
- Less customization and control
3.2. Private IaaS
Private IaaS offers cloud infrastructure that is dedicated to a single organization. It can be hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider but not shared with others. This option provides greater control, enhanced security, and compliance, which is ideal for the finance or healthcare industries.

Benefits:
- Greater control and privacy
- Custom security configurations
- Better performance consistency
Considerations:
- Higher costs
- More management responsibility
3.3. Hybrid IaaS
Hybrid IaaS combines the best of both worlds by integrating public and private cloud resources. This model allows businesses to keep sensitive operations in a secure private environment while taking advantage of the scalability and affordability of the public cloud for less critical workloads.
Benefits:
- Flexible workload management
- Cost optimization
- Balances control and scalability
Considerations:
- More complex to set up and maintain
- Requires strong integration and security planning
4. Advantages of IaaS

One of the biggest reasons businesses are moving to the cloud computing infrastructure model is the flexibility and efficiency that Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) brings. Let’s explore the key benefits that make IaaS a top choice for modern organizations:
- Cost efficiency & pay-as-you-go model: Forget massive upfront investments in physical servers and networking gear. With IaaS, you only pay for what you use—no more, no less. The pay-as-you-go pricing model means you can align your IT spending directly with your usage, making budgeting easier and cutting down on wasted resources. This is especially valuable for startups and businesses with fluctuating demands.
- Scalability and flexibility: Need to ramp up during peak traffic? No problem. Want to scale down during off-seasons? Easy. IaaS platforms allow you to scale your infrastructure on demand, giving you complete control to adjust resources based on real-time needs. Scalability is built in, whether you’re testing a new product or expanding globally.
- Reduced physical hardware management: Managing on-premises hardware is expensive and time-consuming. With IaaS, the cloud provider takes care of the physical infrastructure, so your team can focus on what matters—innovation, not server maintenance. Say goodbye to server rooms, overheating issues, and surprise hardware failures.
- Accessibility and remote management: Access your infrastructure anytime, from anywhere. Through web-based dashboards and APIs, IaaS allows remote teams to monitor, update, and manage resources without being tied to a physical location. In today’s remote-first world, this level of accessibility and control is a massive advantage.
5. Disadvantages of IaaS

While Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) offers a lot of freedom and flexibility, it’s not without its challenges. Like any technology solution, it comes with trade-offs that businesses should carefully consider before jumping in. Let’s take a moment to discuss some of the typical downsides:
- Potential security concerns: Even though major IaaS providers like AWS and Azure invest heavily in security, you still operate in a shared cloud infrastructure. That means sensitive data is hosted off-site, raising concerns about data privacy, compliance, and cyber threats. Organizations in regulated industries (like finance or healthcare) often need to implement extra layers of protection to meet standards.
- Dependence on Internet connectivity: Since IaaS is delivered over the Internet, your infrastructure is only as reliable as your connection. Any downtime in your network—or your provider’s—can disrupt access to applications, services, or data. In regions with spotty connectivity, this can become a serious operational risk.
- Limited control over infrastructure: With IaaS, you’re not managing the physical infrastructure, which is great for convenience, but it also means you have less direct control over hardware configurations, server placement, or backend updates. For highly specialized workloads, this lack of customization can be limiting.
- Possible vendor lock-in: Switching from one IaaS provider to another isn’t always smooth sailing. Different providers may use unique tools, APIs, or configurations, making migration complicated and costly. This vendor lock-in risk means you’ll want to think long-term when choosing a provider and build systems with flexibility in mind.
6. Use cases for IaaS

Now that we’ve covered the what, how, and why of Infrastructure as a Service, let’s talk about where in the digital world IaaS shines brightest. The answer is just about anywhere. IaaS supports many business needs with speed and simplicity, from scrappy startups to global enterprises.
- Hosting websites and applications: One of the most common uses of IaaS is hosting websites and web applications. Need to launch an e-commerce store or build a customer portal? With IaaS, you can spin up servers, allocate storage, and scale traffic handling capacity in minutes. There is no need to manage the hardware for you. You focus on delivering a great user experience.
- Big data analysis: Data is the new oil that needs serious processing power. Enter IaaS. With virtually unlimited computing capacity, IaaS lets businesses run complex big data analysis without investing in expensive on-site infrastructure. Whether you’re analyzing customer behavior, crunching scientific data, or training machine learning models, IaaS brings horsepower.
- Development and testing: Developers love IaaS because it offers a flexible, low-risk environment for building and testing applications. Want to try a new framework? Simulate different user scenarios? Clone your production environment in a sandbox? IaaS makes everything possible, without messing with your core systems or breaking the budget.
- Disaster recovery solutions: Downtime is a nightmare. IaaS helps businesses set up robust disaster recovery systems that can kick in instantly if something goes wrong. By replicating data and systems in the cloud, you can recover quickly from unexpected events—whether a server crash or a natural disaster without losing critical information.
7. Conclusion
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) offers a flexible, cost-effective way to build and manage IT infrastructure without the hassle of physical hardware. With benefits like scalability, remote access, and pay-as-you-go pricing, it’s a powerful solution for businesses of all sizes.
However, don’t overlook potential challenges like security risks or vendor lock-in. Choosing the right IaaS provider means balancing performance, support, and long-term goals. Whether it’s AWS, Azure, or a hybrid solution, pick what best aligns with your needs. IaaS isn’t just a tech upgrade—it. It’s a more innovative way to grow.




