
Enterprise software programs are essential tools that empower large companies to operate at peak efficiency. It enhances productivity, automates processes, and facilitates data-informed choices. This software is essential for managing operations, improving workflows, and connecting different company parts.
Businesses of all sizes use enterprise software to make their operations smoother, increase productivity, and stay competitive. This article looks at the various types of enterprise software, how it is developed, and what to consider when choosing the right software for your business.
1. What is enterprise software development?
Developing enterprise software is a specialized endeavor, going far beyond simple coding. It’s a strategic process dedicated to producing bespoke digital tools that address the intricate demands of a business.
Unlike mass-market software, which aims for broad appeal, enterprise software development is precisely engineered to refine internal workflows, boost output, and achieve specific strategic aims within a defined organization.

1.2. Phases of development
This method, designed for both immediate effectiveness and lasting impact, encompasses several unique phases:
Detailed business analysis (planning):
This initial stage thoroughly examines the enterprise’s current operational framework. We delve into identifying not just apparent issues but also critical bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas ripe for advancement.
This analysis translates into defined enterprise software development goals, ensuring the final product aligns perfectly with the corporate strategy.
This is the cornerstone of the project, guaranteeing the software serves a genuine and valuable purpose.
Intuitive digital environment creation (design):
The design phase focuses on creating a digital space that is effective and easy to use. This involves crafting interfaces that are easy to navigate and constructing robust architectural foundations that show the software’s future growth.
The objective is to provide a fluid user experience that encourages adoption and amplifies productivity. We are building a virtual workspace that empowers users.
Transforming concepts into functionality (development):
This is the point where the vision becomes tangible. Employing low-code development platforms for enterprise software can accelerate the creation of custom solutions while maintaining scalability and flexibility.
This is about writing code and finding innovative solutions to complex business problems. The focus is building a strong, flexible system that can grow and change within the organization.
Comprehensive performance verification (testing):
Before implementation, the software undergoes rigorous testing to pinpoint and resolve potential vulnerabilities or defects. This software test ensures the software is reliable and performs well. We execute thorough testing to mimic real-world situations, providing a stable and smooth user experience. This phase focuses on building confidence in the final product.
Controlled system integration (deployment):
Implementing enterprise software requires careful planning to avoid disrupting business operations. The goal is to smoothly integrate new software, such as business intelligence (BI), enterprise resource planning (ERP), or customer relationship management (CRM), into the existing IT system of the organization.
This phase ensures a smooth transition and rapid realization of the software’s value.
Ongoing refinement and adaptation (maintenance):
Enterprise software is not a static entity. It requires continuous upkeep, updates, and optimization to remain practical and relevant. This includes addressing bugs, implementing new functionalities, and adapting to changing business needs.
This dedication to continuous improvement ensures the software remains a valuable and enduring asset for the organization.
Read more >>>> How to Choose a Software Development Company?
2. Key considerations in enterprise development
Building robust enterprise software isn’t just about code but strategic foresight. Key considerations that separate transformative solutions from costly missteps include:
Scalability: Future-proofing for exponential growth:
In a changing market, businesses need flexible software development. To choose the best enterprise software for managing your business, pick a solution that can handle more users and significant amounts of data without losing performance.
Fortress-level security: Safeguarding intellectual capital:
In an era of escalating cyber threats, security is non-negotiable. Implementing robust security protocols, including Security Information Event Management (SIEM) systems, is paramount to protecting sensitive data and maintaining business continuity.
Seamless ecosystem integration
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) and customer relationship management (CRM) software must integrate flawlessly with existing IT systems to avoid operational bottlenecks. Business process management (BPM) ensures smooth integration and data flow across systems.
Strategic development methodologies
From DevOps’s iterative agility to Waterfall’s based precision, choosing the proper improvement method is crucial. Aligning the approach with project complexity and business objectives ensures optimal resource allocation and timely delivery.
Looking for a Tech Partner Who Delivers Real Results?
We provide tailored IT solutions designed to fuel your success. Let`s map out a winning strategy. Starting with a free consultation.
Connect with an ExpertRead more >>> 9 Benefits of SaaS: Why Businesses Are Making the Switch
3. 18 types of enterprise software
Enterprise software is essential for modern businesses. It helps streamline processes, increase efficiency, and improve decision-making. Here are the main types of enterprise software, what they do, and some key examples:
3.1. Business Intelligence (BI)
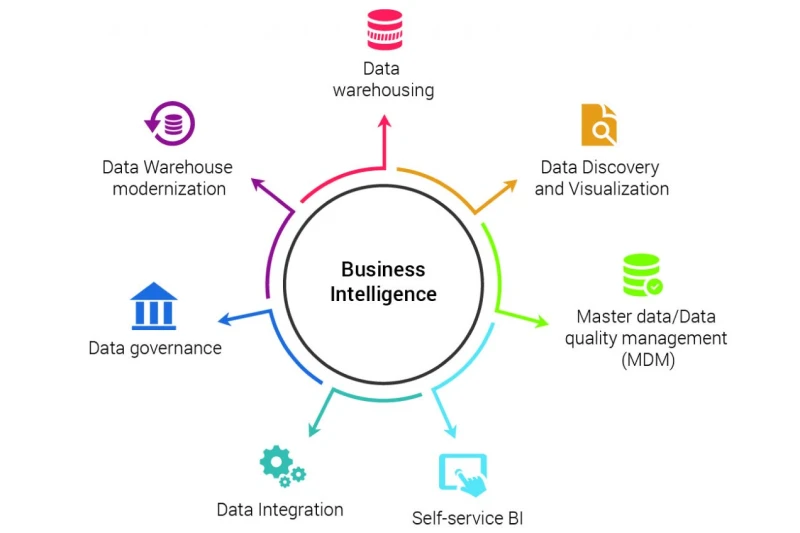
Business Intelligence software (BI) helps organizations convert raw data into meaningful insights. By aggregating and analyzing data from multiple sources, these tools enable businesses to identify trends, optimize performance, and make data-driven decisions.
Advanced BI platforms provide real-time dashboards, predictive analytics, and AI-powered recommendations.
Examples include Microsoft Power BI (seamless Microsoft integration), Tableau (intuitive data visualization), and Looker (cloud-based analytics).
3.2. Business Process Management (BPM)
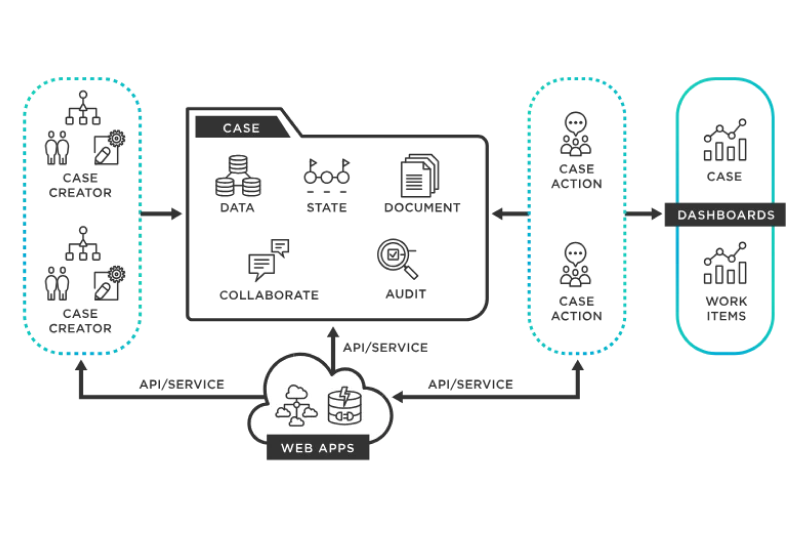
BPM software automates and optimizes business workflows to improve efficiency and consistency. By mapping out processes, identifying inefficiencies, and applying automation, BPM solutions minimize bottlenecks and enhance cross-departmental collaboration.
Industries like finance, healthcare, and logistics use BPM to streamline compliance and service delivery.
Examples include Appian (low-code automation), Pega (AI-driven process optimization), and Nintex (workflow automation).
Read more >>> 4 Types of Offshore Development Centers: Which One is Right for You?
3.3. Content Management Systems (CMS)
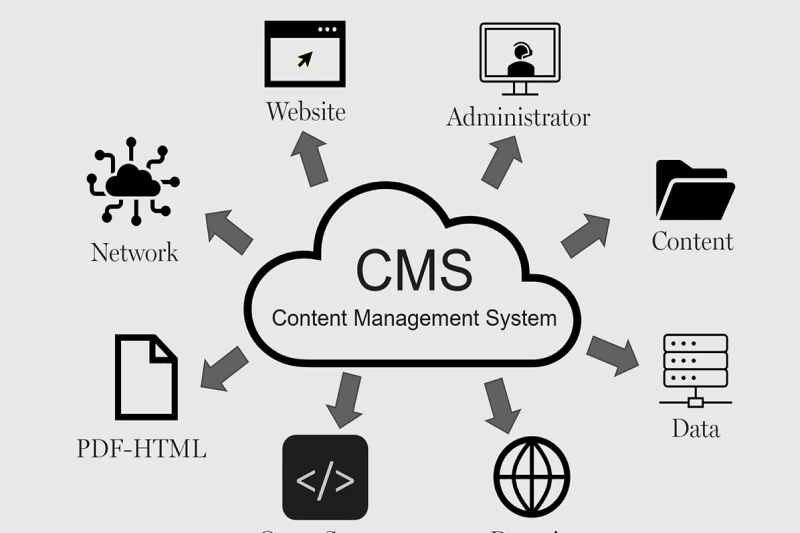
A CMS allows organizations to create, organize, and submit virtual content material without requiring technical expertise. These platforms power websites, blogs, eCommerce stores, and internal knowledge bases.
Advanced CMS platforms offer SEO tools, multichannel publishing, and workflow automation to simplify content distribution. Examples include WordPress (powers 40% of the web), Drupal (robust security), and Contentful (API-first headless CMS).
3.4. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
CRM software centralizes customer interactions, helping businesses improve sales, marketing, and support strategies. Features like automated lead tracking, sales forecasting, and customer segmentation allow companies to personalize outreach and enhance customer retention.
Choosing from the top CRM systems for businesses ensures sales teams operate efficiently.
Examples include Salesforce (enterprise CRM leader), HubSpot (user-friendly inbound marketing), and Zoho CRM (cost-effective for small businesses).
3.5. Database Management Systems (DBMS) & Master Data Management (MDM)
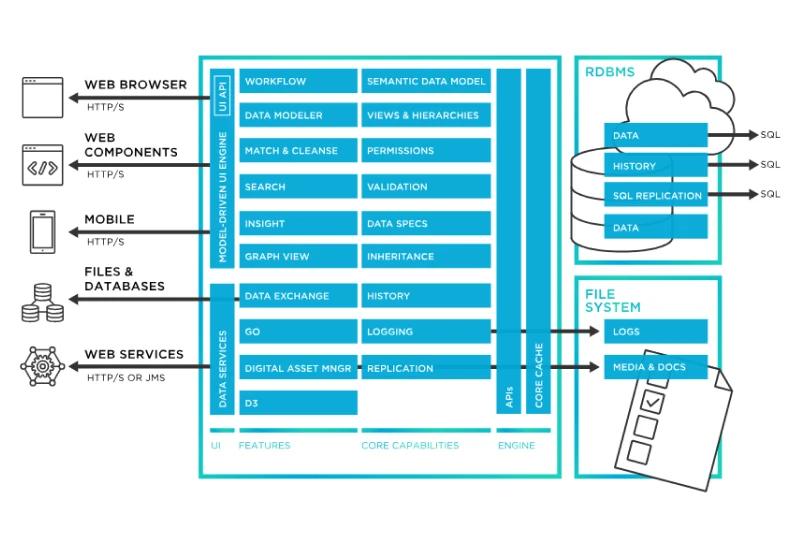
DBMS solutions store and manage structured data efficiently, ensuring data integrity and accessibility.
MDM complements DBMS by ensuring a unified and accurate data repository across different departments. Database management systems for enterprises help businesses handle vast amounts of data securely and efficiently.
These systems are essential for analytics, business intelligence, and regulatory compliance.
Examples include MySQL (popular open-source DBMS), Oracle DB (enterprise-grade scalability), and Microsoft SQL Server (robust security features).
3.6. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
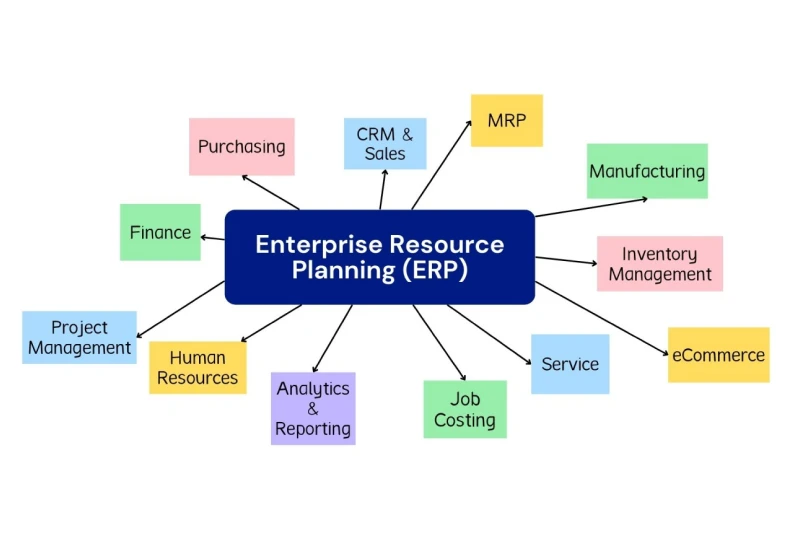
ERP software connects key business functions through a unified system, streamlining financial management, workforce operations, procurement, logistics, and product development. By integrating data across departments, it eliminates silos and provides greater visibility into business processes. Companies leverage ERP solutions to boost efficiency, optimize resource utilization, and maintain regulatory compliance.
A major advantage of enterprise resource planning (ERP) is its ability to consolidate critical data, ensuring smooth coordination across various departments while improving financial oversight.
Notable ERP providers include SAP, known for its dominance in enterprise-level ERP, Oracle ERP, offering comprehensive financial and supply chain management tools, and Microsoft Dynamics 365, a flexible, cloud-based ERP solution.
3.7. Enterprise Asset Management (EAM)
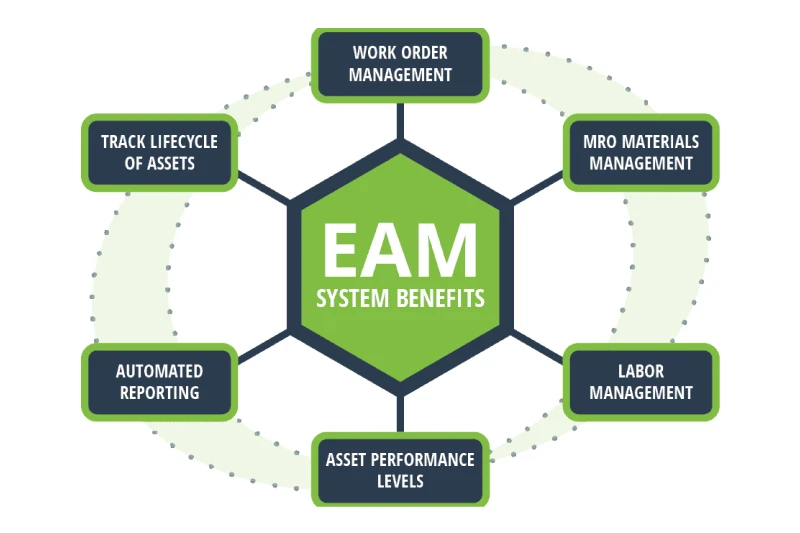
EAM software assists organizations in monitoring, managing, and enhancing physical resources like equipment, transportation, and facilities. Features like predictive maintenance and asset lifecycle tracking help minimize downtime and extend asset longevity.
Examples include IBM Maximo (AI-driven asset management), Infor EAM (industry-specific solutions), and SAP EAM (integrated with SAP ERP).
3.8. Human Resource Management (HRM)
HRM platforms streamline workforce management, covering recruitment, payroll, performance tracking, benefits administration, and compliance. Many HRM solutions now incorporate AI for talent acquisition and employee engagement insights.
Instances include BambooHR (perfect for small companies), Workday (top-tier HR and finance solutions), and ADP Workforce Now (automated payroll and benefits).
3.9. Knowledge Management (KM)
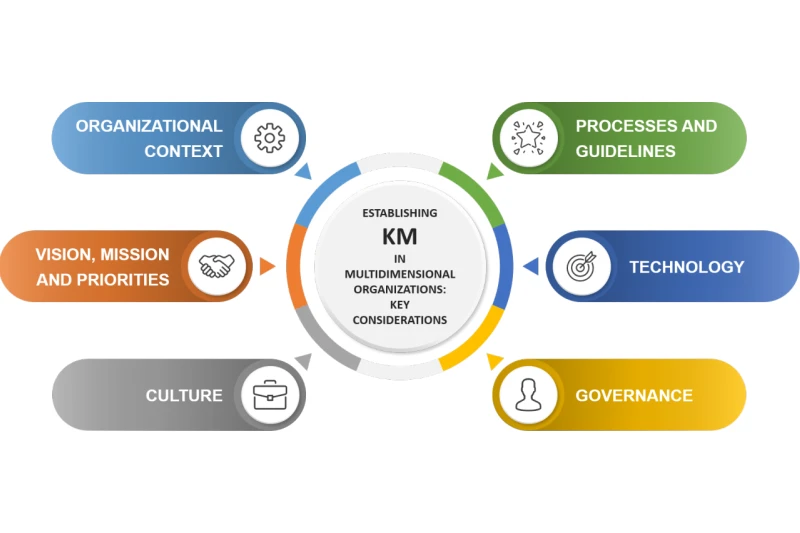
KM software consolidates and centralizes organizational knowledge, allowing employees to easily access information. This is crucial for businesses with remote teams, extensive documentation, or technical support needs.
Examples include Confluence (collaborative documentation), SharePoint (enterprise document management), and Guru (AI-powered knowledge retrieval).
3.10. Low-Code Development Platforms (LCDP)
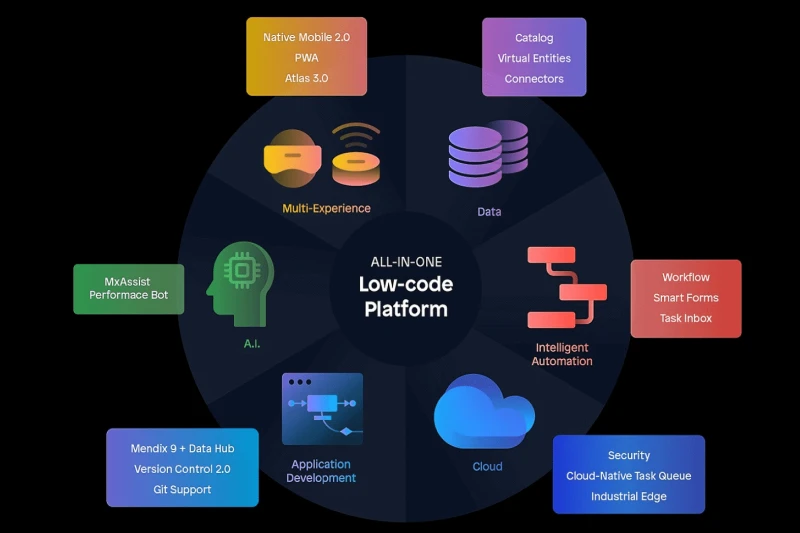
Low-code development platforms (LCDPs) simplify application development by allowing businesses to create software with minimal coding. These platforms reduce reliance on IT teams by offering visual development environments, drag-and-drop functionality, and AI-powered automation. As a result, businesses can accelerate software deployment, lower development costs, and quickly adapt to market changes.
Examples include Mendix (enterprise-grade app development), OutSystems (scalable low-code solution), and Microsoft Power Apps (seamless Microsoft integration).
3.11. Product Data Management (PDM)
PDM software helps businesses organize, control, and track product-related data throughout its lifecycle. This is particularly essential in engineering and manufacturing, where teams need seamless collaboration.
Some widely used PDM solutions include Autodesk Vault, which manages CAD files; Siemens Teamcenter, designed for enterprise-wide product collaboration; and SolidWorks PDM, which optimizes engineering workflows.
3.12. Product Information Management (PIM)
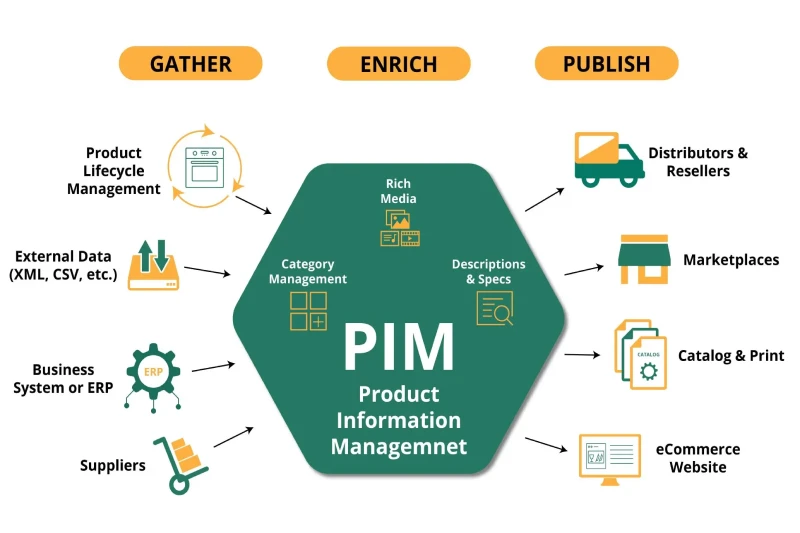
PIM systems enable businesses to maintain and distribute accurate product details across various sales and marketing channels. This is essential for retailers, wholesalers, and eCommerce platforms to ensure product catalog consistency. By centralizing product data, PIM enhances efficiency and reduces errors in descriptions, specifications, and pricing across multiple platforms.
Examples include Pimcore (open-source PIM and MDM), Akeneo (multi-channel product syndication), and Salsify (eCommerce-focused PIM).
3.13. Product Lifecycle Management (PLM)
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) software oversees a product’s journey from initial concept and design to manufacturing, market release, and eventual retirement.
It fosters collaboration among design, engineering, and production teams while ensuring compliance with industry regulations and quality standards. Businesses use PLM solutions to streamline product development and maintain operational efficiency across different stages.
Examples include Dassault Systèmes (leader in PLM for aerospace and automotive), PTC Windchill (cloud-based product lifecycle management), and Siemens PLM (integrated with industrial automation).
3.14. Supply Chain Management (SCM)
Modern supply chain management (SCM) software integrates artificial intelligence to improve demand forecasting, risk assessment, and logistics planning. These tools help businesses anticipate market fluctuations, optimize inventory levels, and mitigate potential disruptions.
Key SCM solutions include SAP SCM, tailored for enterprise-wide supply chain operations, Oracle SCM, which incorporates AI-driven warehouse and logistics management, and Blue Yonder, providing real-time analytics to enhance supply chain agility.
3.15. Software Configuration Management (SCM)
SCM tools track code changes, maintain version control, and facilitate collaboration among software development teams. These solutions are critical for managing software releases and mitigating deployment risks.
Examples include Git (industry standard for code repositories), Subversion (centralized version control), and Perforce Helix (enterprise-scale development teams).
3.16. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
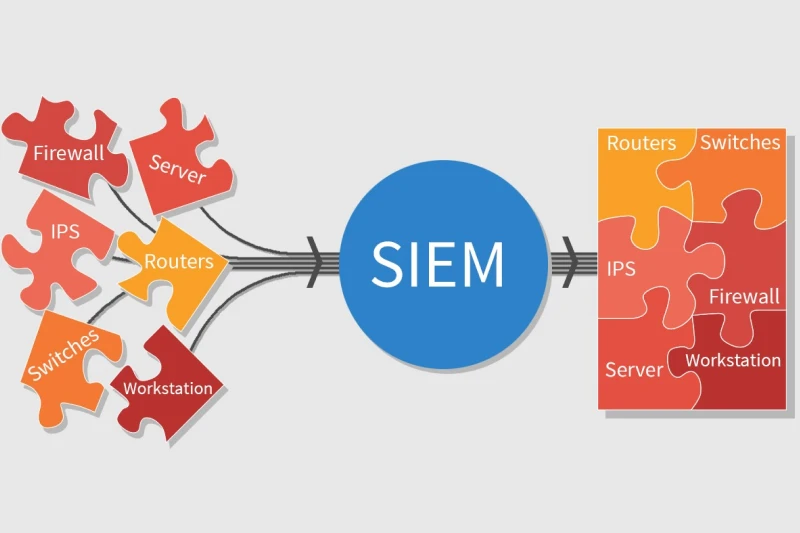
SIEM platforms help organizations detect and respond to cybersecurity threats in real-time by analyzing security logs from various sources. These systems aggregate and correlate data from networks, servers, and applications to identify anomalies and potential breaches, enhancing overall cybersecurity resilience.
Examples include Splunk (AI-powered threat detection), IBM QRadar (enterprise cybersecurity analytics), and ArcSight (comprehensive SIEM security solution).
Read more: 13 Best AI Languages for Machine Learning & Deep Learning
3.17. Intrusion Detection & Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS)
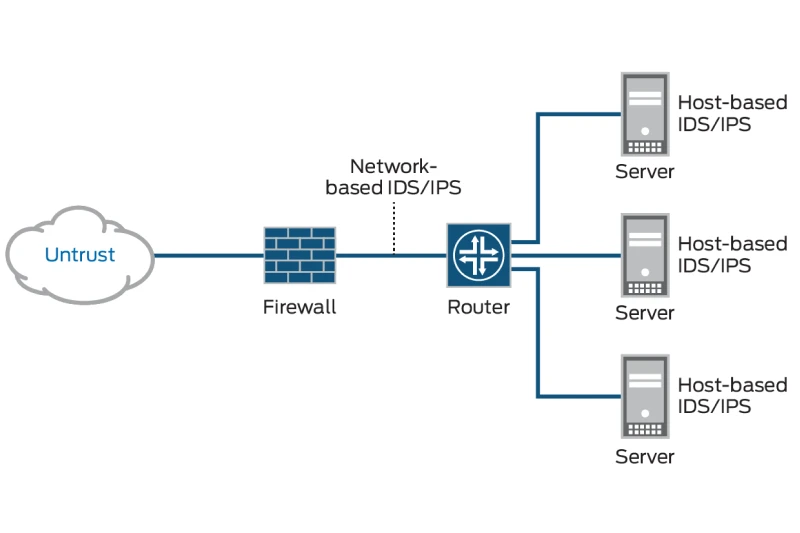
IDS and IPS solutions monitor network traffic to detect and mitigate cybersecurity threats. IDS tools analyze incoming data for anomalies, while IPS actively blocks malicious activities before they reach critical systems.
Examples include Snort (a popular open-source IDS), Palo Alto Networks IPS (advanced threat mitigation), and Cisco Firepower (network security solution).
3.18. Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
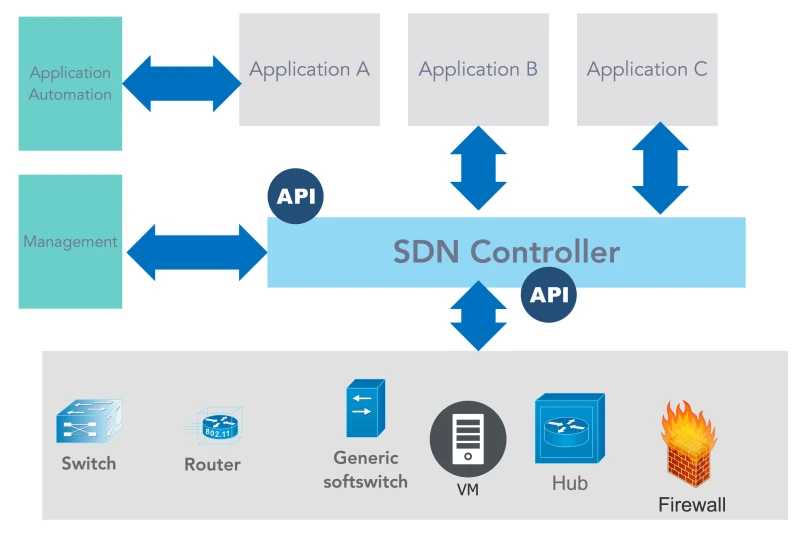
SDN transforms network management into a virtualized format, enhancing flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Instead of relying on traditional hardware-based networks, SDN enables software-driven traffic flow control and security policies.
Instances include VMware NSX (data center network virtualization), Cisco ACI (networking based on intent), and Juniper Contrail (SDN for cloud environments).
4. Conclusion
Type of Enterprise software is critical to modern business operations, driving efficiency, automation, and scalability.
Choosing the right answer involves confidently assessing business needs, ensuring compatibility with existing systems, and staying well-informed about emerging technology trends.


