Did you know that over 90% of the world’s data was created in just the last two years? With the rise of Data Science and Data Analytics careers, many businesses are using data to drive decisions and solve problems faster. However, there is often confusion about the difference between Data Science and Data Analytics. While both deal with data, the roles, skills, and career opportunities differ significantly.
In this blog, we’ll clear up the confusion and help you understand which path suits your career goals and interests. Whether you’re aiming for a Data Scientist career or looking to excel as a Data Analyst, both paths are rewarding and in high demand.
1. What is Data Science?
Data Science is an interdisciplinary field that uses machine learning, predictive modeling, and artificial intelligence to extract insights from complex and large datasets.
It combines math, coding and real-world knowledge to answer hard questions. Data scientists don’t just report what happened, they figure out why it happened, and more importantly, what might happen next.
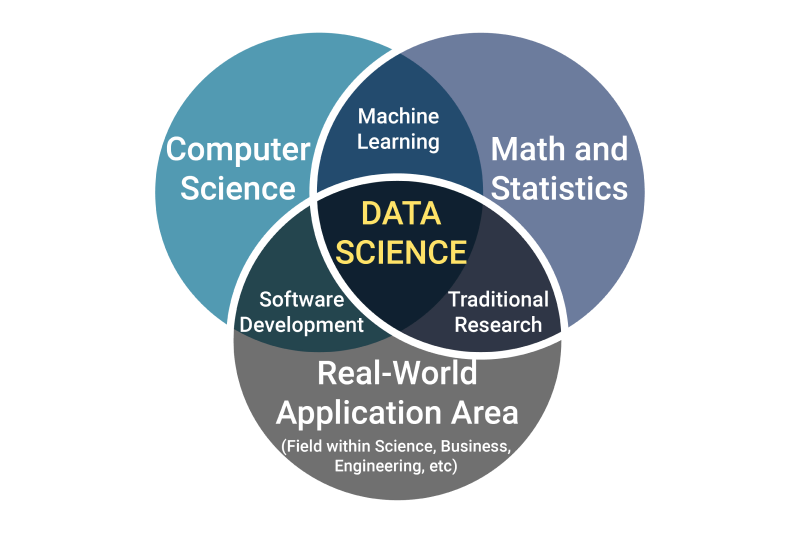
So what Data Scientists do:
- Build smart models that predict outcomes.
- Use machine learning to find hidden patterns.
- Analyze big, messy data sets to solve complex problems.
Real-life examples of data science:
- Banks use it to detect fraud before it causes damage.
- Netflix uses it to suggest movies and shows you might like
- Self-driving cars rely on it to recognize road signs, people and other vehicles.
Common tools used: Many data scientists write code in Python or R. They often use machine learning libraries like TensorFlow, and tools like Apache Spark to handle huge datasets quickly.
Read more >>> What Is Data Integration? Learn How It Powers Business Growth
2. What is Data Analytics?
Data analytics is about understanding what already happened, why it happened, and what it means for business.
It focuses on using data to spot trends, find problems and support decision-making. While data science looks forward, data analytics looks at present and past to guide action.

So, what does a data analyst do?
A data analyst reviews reports, builds dashboards and turns raw data into clear insights. They help teams and leaders understand how the business is performing, what’s working, what’s not, and where to improve.
Their job is less about prediction and more about clarity. They explain the story behind the numbers.
Examples of data analytics in action:
- A sales team tracks monthly revenue and finds which product sells best.
- A marketing team checks which campaign brought in the most leads.
- A company reviews customer feedback to improve its service.
Common tools used: Most data analysts work with SQL to get data from databases. They also use Excel, Tableau, or Power BI to visualize the results and present them clearly to others.
Read more >>> DevOps vs. DevSecOps: Understanding the Key Differences
3. Key differences between data science and data analytics
While both data science and data analytics work with data, their focus, methods, and goals are different. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Aspect | Data Science | Data Analytics |
| Scope & Focus | Broader, predictive, future-oriented | More focused, descriptive, present/past-oriented |
| Key Skills | Advanced programming (Python, R), machine learning, big data frameworks | SQL, data visualization tools (Tableau, Power BI), business acumen |
| Objectives | Discover new insights, build predictive models | Analyze past data, optimize current processes |
| Data Type | Unstructured, large-scale data | Structured, manageable datasets |
| Complexity | More complex, requires technical expertise | More accessible, less technical |
3.1 Skills required for data science and data analytics
The skills needed for data science and data analytics are quite different. Here’s a breakdown of what each path requires:
3.1.1 Data science skills
- Programming: data scientists use languages like Python and R to write code for data analysis and machine learning models.
- Machine learning (ML) and AI: understanding algorithms and models used to make predictions.
- Statistical modeling: data scientists need a strong understanding of statistics to analyze data and build models.
- Data wrangling & preprocessing: cleaning and organizing raw data to make it usable for analysis.
3.1.2 Data analytics skills
- SQL: data analyst must be proficient in QQL to query and mange databases.
- Data visualization: Tools like Tableau, Power BI, and Excel are used to create clear, visual representations of data
- Statistical analysis: while less advanced than in data science, basic stats help analysts draw conclusions from data.
- Business communication & storytelling: data analysts need to present their findings in a way that is understandable and valuable for business decision-making.

3.2 Career opportunities and job responsibilities
Choosing between Data Science vs Data Analytics often comes down to the specific roles and career paths available in each field. While both fields offer great career opportunities, their responsibilities differ significantly. Below, we’ll look at the key roles in both Data Science and Data Analytics, including the responsibilities, skills required, and potential career progression.
| Role | Data Scientist | Data Analyst |
| Job Titles | Data Scientist, ML Engineer, AI Specialist | Data Analyst, Business Intelligence (BI) Analyst, Data Consultant |
| Responsibilities | Build models and algorithms, machine learning, collaborate with teams, solve complex data problems | Create reports and dashboards, analyze KPIs, support decision-making |
| Skills Required | Programming (Python, R), ML, AI, statistical modeling, big data frameworks | SQL, data visualization (Tableau, Power BI), business communication |
| Salary Range | Generally higher due to advanced skills | Competitive, but usually lower than data scientists |
| Career Path | Start as an analyst, move into machine learning or AI roles | Transition into data science with programming and ML skills |
Read more >>> Difference between verification and validation in software testing
4. Which path is right for you?
When it comes to choosing between the difference between data science and data analytics, it all depends on what interests you the most and what skills you want to develop. Here are some things to think about when deciding which path is the right one for you:
4.1 Factors to consider
- Coding and technical challenges
- If you enjoy coding, building algorithms, and solving complex problems, data science might be the better fit for you.
- On the other hand, if you like working with data to create reports and help businesses make smarter decisions, data analytics could be the path you’re looking for.
- Business vs technology focus
- Data analytics is great for people who prefer applying data to improve business processes and drive decisions.
- If you’re more excited about exploring new technologies and building predictive models, data science is probably a better fit.
- Your educational background
- Typically, data science requires a background in STEM fields (Science, Technology, Engineering, Math).
- Data analytics has a broader appeal with professionals coming from all sorts of fields, including business, economics, and engineering.
4.2 Pros and cons
Which path is better for you? The world of data is full of exciting opportunities, but with Data Science and Data Analytics offering different career trajectories, it’s important to understand the pros and cons of each. While both fields are crucial for businesses today, they come with their own sets of benefits and challenges.
| Path | Pros | Cons |
| Data Science | High impact, complex, innovative | Steep learning curve |
| Data Analytics | Practical, directly benefits business decisions | Less focus on advanced tech |
5. Conclusion
In conclusion, Data Science and Data Analytics are two essential roles in today’s data-driven world, each with its own unique focus and skill set. Understanding the difference between Data Science and Data Analytics can help you choose the right path for your career or business needs. Whether you choose to dive into the complexities of Data Science or help businesses make informed decisions with Data Analytics, both paths offer exciting opportunities.
At Stepmedia Software, we’re here to help you explore and excel in these fields with tailored solutions and expert guidance. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to scale your business with data, we’ve got the tools and expertise you need to succeed.
Ready to dive deeper? Visit Stepmedia Software to learn more about how we can support your data journey.