What is outsource company? Simply put, it’s a business that provides outsourcing services to other companies. Outsourcing means hiring a third-party service provider to handle specific tasks instead of managing them in-house. This can include IT outsourcing services, customer support outsourcing, or even manufacturing outsourcing. Many companies choose outsourcing to reduce costs, access specialized skills, or improve efficiency.
1. Types of outsourcing
Businesses looking to optimize costs and efficiency must understand what is outsource company and the types of outsourcing available. The three primary models: onshore, nearshore, and offshore outsourcing, offer unique benefits depending on location, expertise, and budget.
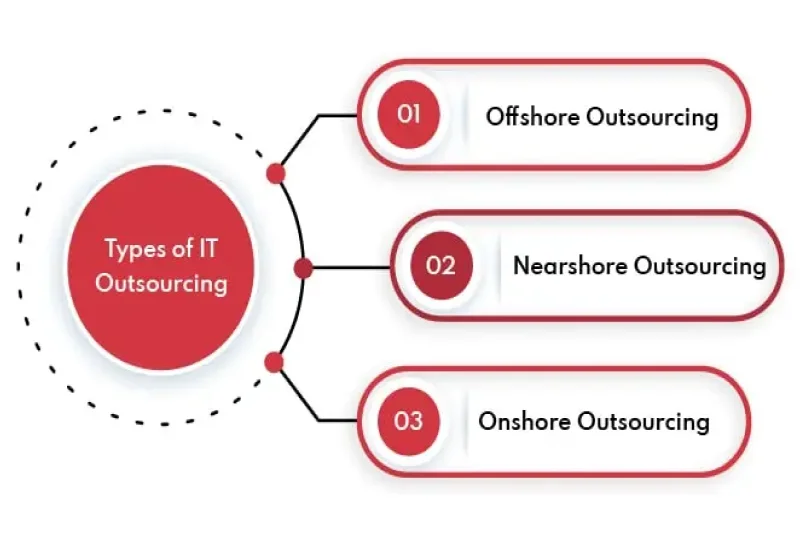
1.1. Onshore outsourcing
Companies that prefer to work with local providers opt for onshore outsourcing. This means hiring a third-party service provider within the same country. It eliminates language barriers, ensures compliance with national regulations, and allows for closer collaboration.
For example, a financial firm in the U.S. might outsource its IT support to a domestic tech company instead of managing an in-house team. This approach maintains quality and data security while reducing overhead costs. Many businesses looking for reliable partners consider this model when deciding outsource company best suits their needs.
Read more >>> Difference Between Onshore and Offshore Software Development
1.2. Nearshore outsourcing
For businesses seeking lower costs without major time zone differences, nearshoring and onshoring are often compared. Nearshore outsourcing destinations are neighboring countries that offer skilled professionals at competitive rates.
A common example is U.S. companies outsourcing customer support to Mexico or Canada. Similarly, European businesses frequently partner with service providers in Eastern Europe. This model helps companies maintain operational efficiency while benefiting from reduced expenses and a familiar business culture.
1.3. Offshore outsourcing
Some businesses prioritize cost savings and specialized expertise over proximity, making offshore outsourcing an attractive option. This involves outsourcing services to a provider in a distant country where labor costs are lower.
Popular destinations include the Philippines Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) industry for customer service and India IT outsourcing for software development. Many global companies outsource call center operations to the Philippines due to its skilled workforce and English proficiency. Similarly, tech firms partner with Indian software developers to access high-quality IT solutions at a lower cost.
Read more >>> 4 Types of Offshore Development Centers: Which One is Right for You?
2. Outsourcing models
When businesses explore outsourcing models, they need to choose the right approach based on their goals. Understanding different types of outsourcing models explained can help companies decide which structure best fits their needs. Here are four common models:
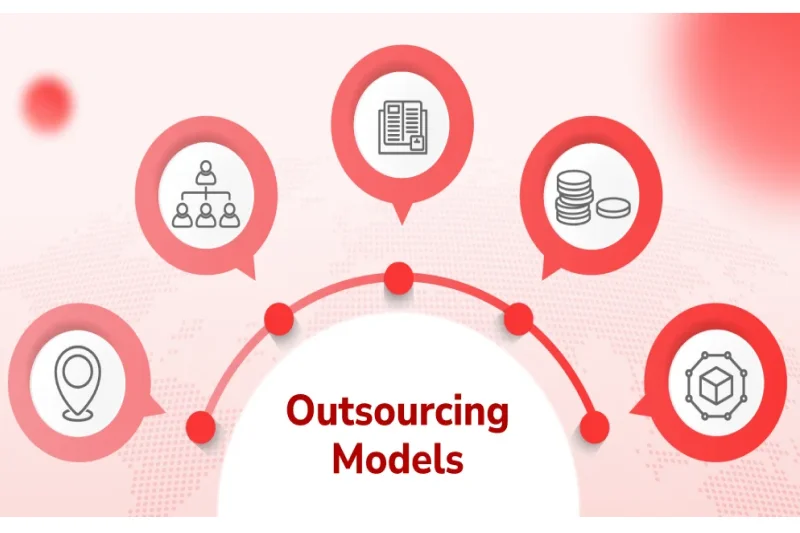
2.1. Project-based outsourcing
This model is ideal for companies that need a team to complete a specific task without long-term commitments. Businesses define their requirements, and a third-party service provider delivers the final product.
For example, a company may outsource mobile app development to an external agency. Once the app is complete, the partnership ends. This model works well for short-term projects with clear objectives, making it a practical option when considering outsource company that can handle specialized tasks.
2.2. Staff augmentation
With staff augmentation, businesses hire external professionals to support their in-house team. These outsourced employees work as part of the company’s existing workforce but remain employed by the service provider.
A common use case is hiring IT developers to work alongside an internal software team for a specific project. This model offers flexibility, allowing businesses to scale their workforce as needed without long-term hiring commitments. Many companies use this approach when looking for outsourcing models that enhance internal operations.
2.3. Development center
A development center is a dedicated team of experts working exclusively for one company, typically in an offshore or nearshore outsourcing destination. This model is best for businesses that need continuous development but don’t want to maintain an in-house team.
For example, a U.S. company might set up a development center in India to handle software engineering. The team works on multiple projects under the company’s direction, offering a cost-effective way to maintain full-time expertise.
2.4. Hosting outsourcing
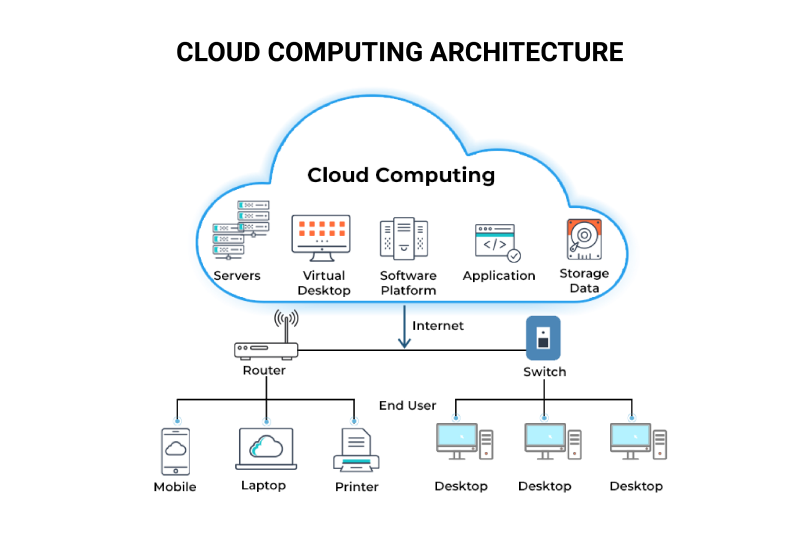
In hosting outsourcing, companies transfer IT infrastructure management to an external provider. This includes cloud computing, data storage, and website hosting.
Many businesses rely on cloud service providers to handle their servers instead of maintaining their own. This model reduces operational costs and ensures high performance and security. It’s a popular option for businesses seeking different types of outsourcing models explained in IT services.
3. Reasons to outsource
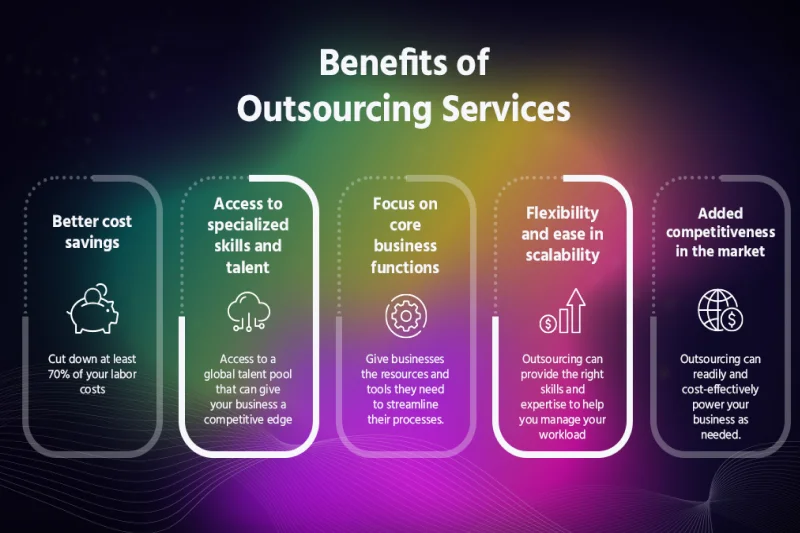
Many businesses choose outsource company solutions to optimize operations, reduce costs, and improve efficiency. The benefits of outsourcing extend beyond financial savings, helping companies gain access to specialized expertise, improve flexibility, and focus on core business functions. Below are key reasons to outsource IT services and other business operations.
3.1. Cost reduction and efficiency gains
One of the biggest cost reduction strategies is outsourcing. Hiring a third-party service provider is often more affordable than building an in-house team. Businesses save money on salaries, training, equipment, and infrastructure costs.
For example, companies that need software development may find India IT outsourcing a cost-effective solution. Hiring an offshore team in India can provide the same level of expertise at a fraction of the cost compared to local developers. Similarly, businesses in need of customer service often turn to the Philippines Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) industry, which offers skilled professionals at competitive rates.
3.2. Access to specialized expertise
Not all companies have in-house specialists for every business function. By outsourcing, businesses can tap into global expertise without the need for costly training programs. Customer support outsourcing, IT outsourcing services, and manufacturing outsourcing are common areas where companies seek external expertise.
For example, a startup without an in-house IT department may outsource cybersecurity and software maintenance to an experienced IT firm. A fashion retailer may outsource production to a manufacturer with expertise in high-quality fabric sourcing. This model allows businesses to gain a competitive advantage by leveraging industry specialists.
3.3. Focus on core business functions
By outsourcing non-core activities, businesses can concentrate on their primary strengths. Handling routine administrative tasks, IT support, or manufacturing outsourcing in-house can be time-consuming and distract from growth strategies. Outsourcing these processes allows companies to focus on core competencies, such as product development, marketing, and customer relationships.
For example, an e-commerce brand may outsource logistics and customer service while focusing on brand growth. A software company may outsource payroll processing so its leadership team can focus on innovation. This aligns with global outsourcing trends, where businesses strategically delegate tasks to improve efficiency.
3.4. Scalability and flexibility
Business needs are constantly evolving, and outsourcing offers companies the ability to scale operations up or down as required. Instead of hiring full-time employees and committing to long-term expenses, businesses can outsource specific tasks based on demand.
For instance, retail businesses often outsource seasonal customer support during peak shopping periods. IT firms may expand their development teams by outsourcing extra programmers for short-term projects. This flexibility helps businesses adapt quickly to changing market conditions.
Want to Integrate Powerful IT Solutions into Your Business?
We provide tailored IT solutions designed to fuel your success. Let`s map out a winning strategy. Starting with a free consultation.
Contact Us4. Pros and cons of outsourcing business processes

While outsourcing provides numerous advantages, it also comes with some risks. The benefits of outsourcing include lower costs, improved efficiency, and access to expert talent. However, challenges like communication barriers, data security concerns, and potential quality issues may arise.
To minimize risks, businesses must carefully select their outsourcing partners. Conducting due diligence, setting clear expectations, and maintaining oversight are essential steps in ensuring outsourcing success.
By understanding the reasons to outsource IT services and other functions, companies can make informed decisions about outsourcing strategies. Whether the goal is cost savings, operational efficiency, or accessing specialized talent, outsourcing remains a powerful tool for business growth.
5. Conclusion
Understanding what is outsource company helps businesses make informed decisions about delegating tasks to external providers. Outsourcing offers many advantages, from cost reduction strategies to improved efficiency and access to specialized expertise. Companies can choose different outsourcing models, such as project-based outsourcing, staff augmentation, or development centers, based on their needs.



























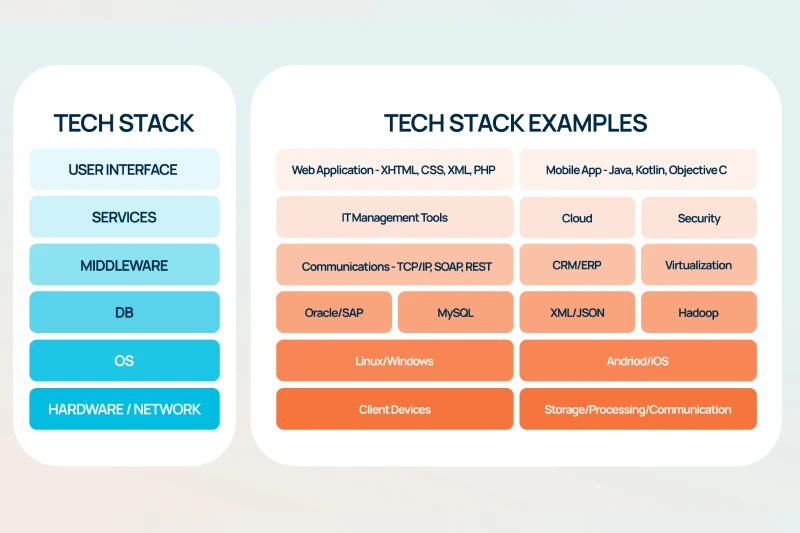














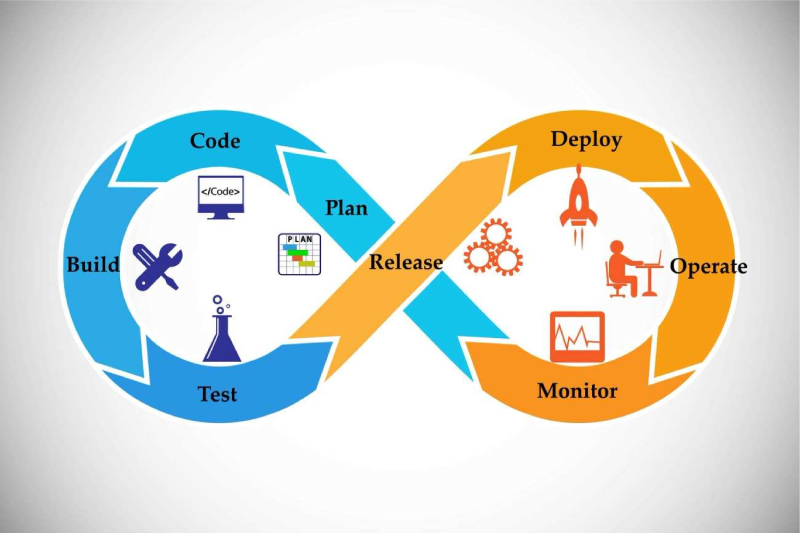




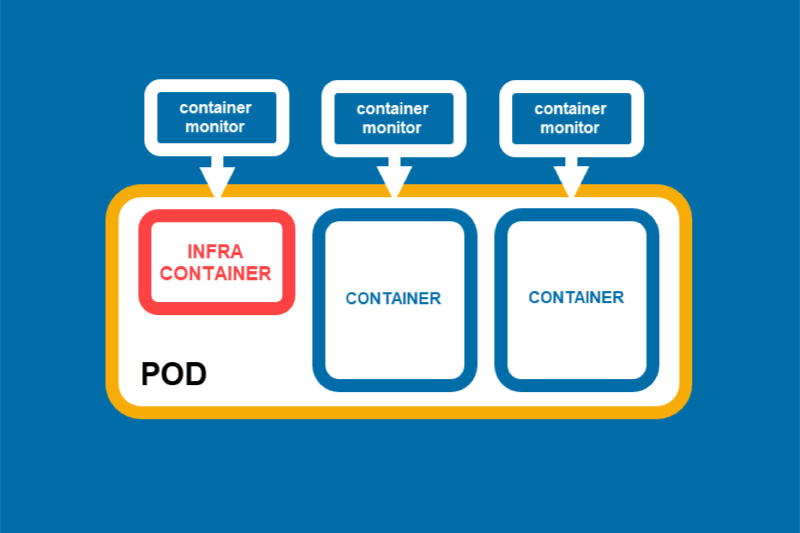
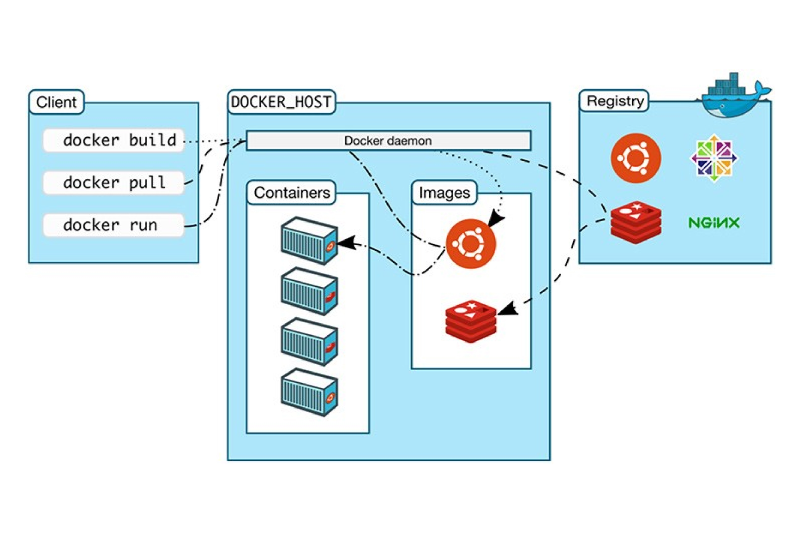
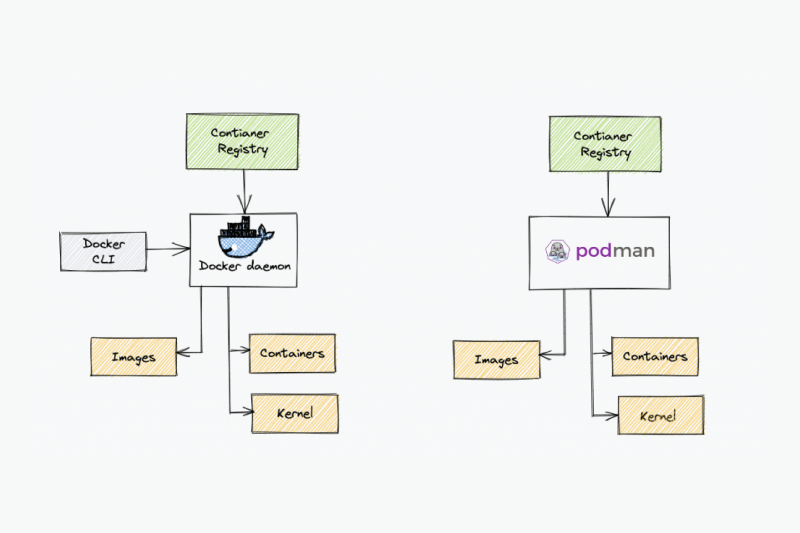
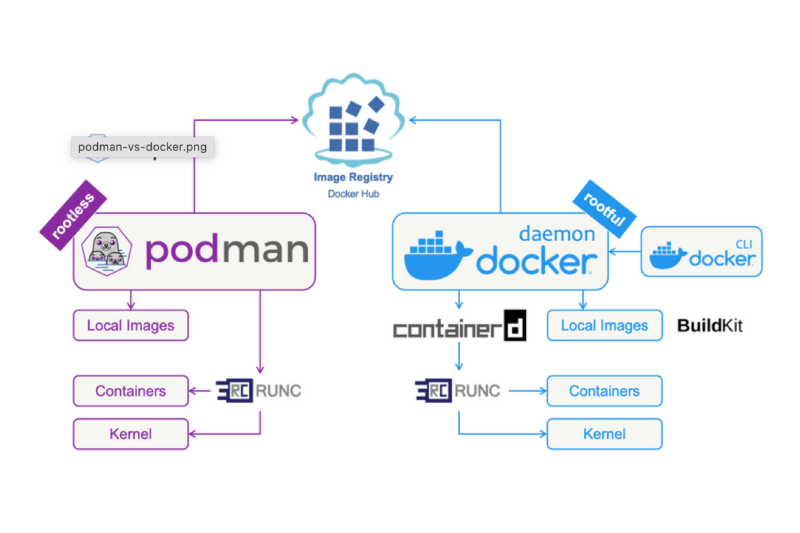
 Containers have revolutionized app development by replacing bulky VMs (Virtual Machine) with lightweight, portable environments. Docker has lengthy been the go-to tool, however Podman is rising as a sturdy alternative. Is it more secure? A better choice?
Containers have revolutionized app development by replacing bulky VMs (Virtual Machine) with lightweight, portable environments. Docker has lengthy been the go-to tool, however Podman is rising as a sturdy alternative. Is it more secure? A better choice?