Golang is the fast programming language inspired by the US-based IT giant Google in 2009. Most of the developers use Go to solve their most modern challenges. It is a simple, effective, and scalable programming language. According to the Stack Overflow Developer Survey, the other important fact that alludes to Golang being one of the fastest-growing programming languages is the 150% increase in usage.
So, what is Golang used for? Go is great for building robust and efficient applications, primarily for cloud computing platforms and microservices architecture. In this post, Stepmedia Software will explain its phenomenal popularity with developers and how its distinctive properties fit the needs of various programming purposes. Golang can be your ultimate life-changer for projects, whether experienced or just starting.
1. What is Golang?
The statically typed, compiled programming language Golang (or just “Go”) is notable for its emphasis on efficiency, concurrency, and scalability. Go makes it easy for developers to construct strong, maintainable programs with its straightforward syntax and clean code structure. Important aspects consist of:

- The built-in goroutines and channels make concurrent programming uncomplicated, providing support for concurrent programming.
- Garbage collection: Fewer memory leaks and improved performance are guarantees of automatic memory management.
- Library of rich standards: Networking, file I/O, and testing are just a few of the many jobs made easier by the extensive built-in packages.
Golang was developed by Googlers Robert Griesemer, Rob Pike, and Ken Thompson in 2009 the reduction problems caused by older programming languages and make them more relevant in modern software engineering. Golang was designed with simplicity, speed, and scalability in mind, and it’s meant for cloud-native applications and microservices.
The simple reason for the attractiveness of Golang is that it had men thrown into its competition: along with great power came the ability to use it easily.
Read more >>>> Golang vs Java: Which Programming Language Should You Choose in 2025?
2. When to use Golang?
Go is a rising star in the programming world. This Google-born language offers a unique blend of simplicity and power. It serves many purposes, making it a versatile tool for many applications. Understanding its strengths and when to use Go helps identify the perfect scenarios where Go excels as the ideal solution.
2.1 Ideal Use Cases for Golang
Go is built for speed. Its lightweight goroutines allow you to handle thousands of concurrent tasks effortlessly, making it a perfect fit for demanding applications. Need a real-time messaging platform that feels instant? Or a web server that can handle millions of requests without breaking a sweat? Go greatly benefits real-time systems, such as live messaging platforms and online gaming servers, where low latency is critical.
Besides, it is the most appropriate option for high-traffic web servers that handle thousands or millions of simultaneous requests without suffering bottlenecks. The performance and simplicity of Go make it the go-to language for all these and many more high-performance applications.
Read more: What is Flask Used For? Key Benefits and Applications
2.2 Comparing Golang with other languages
For a detailed overview of each language’s strengths and best use cases, we encourage you to refer to the comparison table: Golang vs. Python, Java, and C++ to help decide which suits your project needs.
|
Feature
|
Golang
|
Python
|
Java
|
C++
|
|
Performance
|
High-performance, thanks to compiled nature and efficient concurrency.
|
Slower due to its interpreted nature but sufficient for most general purposes.
|
Good performance but is slower than Go due to JVM overhead.
|
Exceptional performance, close to hardware-level efficiency.
|
|
Concurrency
|
Built-in support with goroutines and channels, making concurrency straightforward.
|
Limited built-in concurrency; relies on external libraries like asyncio.
|
Thread-based concurrency is more complex to implement compared to Go.
|
Thread-based concurrency offers full control but with increased complexity.
|
|
Syntax
|
Simple, clean, and easy to learn for new developers.
|
Extremely readable and beginner-friendly; high versatility for scripting.
|
Verbose is compared to Go but highly structured, with strict typing.
|
Complex and verbose, requiring detailed management of resources.
|
|
Compilation/
Execution
|
Compiled language, leading to fast execution and quick startup times.
|
Interpreted, slower at runtime but faster during development cycles.
|
Compiled to bytecode; slower startup but benefits from JVM optimizations.
|
Fully compiled, offering fine-grained control and rapid execution.
|
|
Ecosystem
|
A growing ecosystem with a strong focus on backend, cloud, and microservices.
|
Vast ecosystem for web, data science, and general-purpose applications.
|
A mature ecosystem with strong support for enterprise applications.
|
Established an ecosystem with extensive libraries for system-level and performance-critical tasks.
|
|
Memory Management
|
Automatic garbage collection.
|
Automatic garbage collection.
|
Automatic garbage collection via JVM.
|
Manual memory management or smart pointers for finer control, with a higher risk of memory leaks.
|
|
Platform Independence
|
Cross-platform but requires recompilation for each target.
|
Cross-platform; no recompilation needed.
|
Write once and run anywhere (JVM-based).
|
Cross-platform, but binary needs recompilation for each platform.
|
|
Best Use Cases
|
Cloud computing, microservices, real-time systems, and high-performance applications.
|
Scripting, data science, web development, and rapid prototyping.
|
Enterprise applications, Android development, and systems require a large ecosystem.
|
Game development, system programming, and resource-intensive applications.
|
|
Learning Curve
|
Moderate; simpler than Java or C++.
|
Very easy, ideal for beginners.
|
Steeper than Go and Python but manageable with prior experience.
|
Steep is suited for advanced developers due to low-level complexity.
|
Read more: C# vs Java: Similarities, Differences, and Practical Insights
3. Why use the Go programming language?
Golang has become the peremptory back-end and web development language. Not only because of the developer-friendly features, but also the Golang advantages such strong business capacities afford. But what is Golang used for, and why is it so competent?
3.1 Benefits for Developers
- Improved productivity with Go: More work gets done with Go because it is simple, which helps developers learn without having to spend a lot of time figuring out how to use it. The code is pretty clean, and the compilation is fast, so you can really focus on making great apps within the limits of the streamlined development process that boosts productivity across all areas of app development.
- Making concurrency easy: People usually turn into heat when they multicast. The concurrency model built into Go, on the other hand, makes all jobs easy. With goroutines and channels, you can write scalable apps fast enough to handle heavy workloads, like real-time systems or services with a lot of traffic. When you use concurrency in Go, behaviors are designed to handle complicated processes with stable output.
- Dynamic community: Picking Go is more than just picking a computer language; it connects you with a lively and active community. There are a lot of useful resources in the Golang community, such as tutorials, documents, and forums where developers can talk about and find answers to a wide range of problems. By using Go, you will never be building by yourself. You can ask questions, learn from others, or find people who share your interests.

3.2 Benefits for Businesses
- Expansibility and reliability: Go’s goroutines and channels make concurrent programming easy for multi-tasking and high traffic. Unlike other threading languages, Goroutines allow millions of concurrent operations with almost no overhead, making it ideal for large systems. Global microservices architecture and high-volume web servers work reliably under extreme loads.
- Cost-effectiveness: Since infrastructure costs are directly affected by Go’s efficiency, it saves resources. Go’s speed and multitasking efficiency let applications run efficiently without expensive hardware. Thus, Golang developers can improve performance with few resources but save the organization money.
- Faster time to market: Go’s concise syntax and fast compilation speed allow developers to write, test, and publish apps faster than other programming languages. Development is simpler, and debugging is smoother, so teams can adapt rapidly to market demands, roll out changes, and launch products faster, providing organizations an edge.
3.3 Real-world applications and success stories
There are great strides made in real-world applications by Golang. Today, it is used in most of the best-known companies that have relied on its power to provide a scalable and effective system. Learn why top companies choose Golang through these excellent case studies.
- Google: Google’s own Go is used extensively internally on projects and services like YouTube, Google Cloud, and Kubernetes. Go shines at large-scale systems and distributed environments.
- Uber: Uber uses Go for real-time ride matching and live route optimization. The concurrency in Go allows Uber to build reliable systems that process millions of operations a second.
- Dropbox: Dropbox has moved a large part of the backend from Python to Go. This resulted in performance improvements as well as less cost on servers. Go permits Dropbox to easily scale its way into services with its efficiency and speed of development.
- Twitch: The streaming platform uses Go to power its chat service, which scales to hundreds of thousands of users concurrently while ensuring low latencies. With its concurrency and performance capabilities, Go delivers an unparalleled experience to Twitch users around the globe.
Read more: What is Unreal Engine and Can It Make You a Game Developer?
4. What can you build with Golang?
Golang has the versatility and efficiency of a power tool that one can use to build applications of any kind. Now, let us look more closely at what Golang developers can do with this solid language:

4.1 Web Servers and APIs
Golang is among the best programming languages to use as a high-performing programming language for the web server and RESTful API backend. Due to its efficiency and simplicity, developers can easily handle overwhelming traffic, and thus, Go is widely used for web development. Gin, Echo, and Beego are some of the most popular Go web frameworks. They have extra tools and features that speed up development while ensuring that modern web apps can be scaled and maintained.
4.2 Distributed systems
Currently, the Go programming language is also suited for building distributed systems with built-in concurrency and powerful networking. All these make it relatively easier for scalably fault-tolerant architectures since services can communicate easily. Cloud computing as well as microservices, relish such architectures.
4.3 Command line tools
The simplicity and speed of Go are ideal for writing quick command line tools and utilities. Many developers find Go superior for building automation, debugging, or infrastructure management tools since its speed makes deployment simple.
4.4 Network services
Network programming is where Go tools shine because they are perfect for building network proxies, chat programs, and network services. With a robust built-in standard library and the ability to concurrently execute multiple tasks, this programming offers developers opportunities to write light and speedy services that operate well under thirsty network conditions.
Whether creating scalable web servers or distributed systems or building powerful networking applications, Go has the tools and the performance to carry the concept into real life.
5. What is Golang used for? (specific examples)
As a programming language, Go is a very simple yet powerful tool widely used for concurrency. It exceeds most people’s conception of what can or cannot be done with a programming language because it excels across diverse uses. Here is how the spate of modern development continues today.
5.1 Cloud computing
Golang is laid at the foundation of this new and modern cloud infrastructure which is easily scalable and highly concurrent. A few examples of such tools are mentioned below:
- Docker: The software would deploy the application software into a container.
- Kubernetes: They manage and orchestrate containerized applications under clusters.
- Terraform: Managing the infrastructure as code effectively and having the ability to scale it.
5.2 Web development
With speed plus efficiency, Go is amongst the top-most programming languages that power some of the fastest web servers and back-end systems. Companies like Dropbox and Netflix rely on Go to serve millions of users and provide exceptionally reliable and scalable performance.
5.3 Network programming
Go seems to be a natural and direct answer to almost any of your network programming requirements because of the very rich libraries and concurrency model it implements. It allows developers to create:
- Secure network proxies
- Real-time chat applications
- Distributed systems that perform seamlessly under a high-demand network operation.
5.4 Command-line tools
Fast execution and simplicity make Go an ideal language under which efficient command-line tools are built. Examples of such include the following:
- Hugo: The fast and flexible static site generator.
- Cobra: A library for building feature-rich CLI applications.
5.5 DevOps and site reliability engineers (SRE)
Golang actually works wonders for DevOps and SRE teams: it makes an application run as fast as possible, is most reliable, and meets the requirements of critical tasks. For instance, you can:
- Automate repetitive workflows and increase operational efficiency.
- Provide monitoring systems and perform measurements against key metrics considering uptime and reliability.
- Optimize resource utilization to achieve high availability.
6. Advantages of using Go Programming Language
- Powerful Programming: Golang is a Programming Language that offers the advantages of performance, simplicity and developer friendliness. Here are some of its most popular Golang advantages:
- Performance and efficiency: Thus, the compiled language Golang will run very fast because it will compile code into machine instructions. Its small memory and efficient garbage collection improve execution, which should be well suited to applications that need high performance, low latency, and resource usage.
- Concurrency: This is where Go shines. It provides an in-built concurrency model for its built-in concurrent handling of tasks. With goroutines, you can run many functions simultaneously on very low memory, and channels provide easy communication between them. Such applications as real-time systems and distributed services easily use Go because it is cheaper to scale.
- Simplicity and readability: Golang has a fairly clean and simple syntax and few keywords, making everything readable and maintainable. Hence, Go’s code can be understood quickly and modified without adding complexity to any development aspect.
- Fast compilation: Go indeed has very fast compilation speeds and allows developers to build, test, and deploy applications with minimum overhead. This advances the speed of development and reduces time for the market.
- Strong standard library: The advantages of Go in terms of programmability over many other platforms come from its strong standard library, which encapsulates built-in functionalities-from file I/O and networking to data structures and testing-to really eliminate the need for many external dependencies in development.
- Evolving ecosystem: The Golang community has supported a rapidly growing ecosystem of libraries, frameworks, and tools from widely popular frameworks.
7. Getting Started with Golang
Get ready to start learning Golang. Here is the small yet simple step to get you going to create your first Go program and its learning resources.
7.1 Installation
It is simple, and one can install Go on most operating systems.
- Windows:
1. Get the Go installer from the following address on the web: www.golang.org
2. Run the installation and follow the instructions prompted.
3. Check the installation by running the go version. on the Command Prompt.
- macOS:
1. Download the .pkg file on its official website.
2. Run it and follow the steps.
3. Check your installation by running the go version on Terminal.
- Linux:
1. Get it from www.golang.org (it’s called a tarball).
2. Untar it and add the go binary into your PATH.
3. Verify installation by running the go version.
7.2 Example
Here’s a basic Go program to get started:
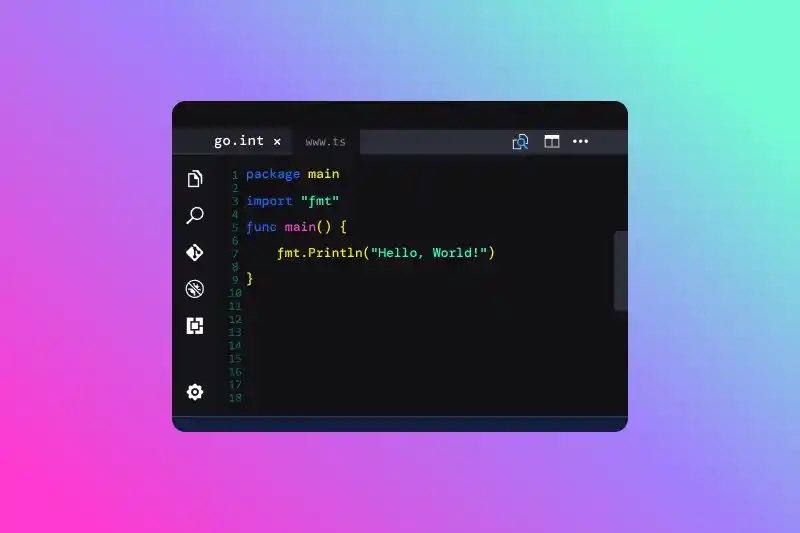
- Save the file as hello.go.
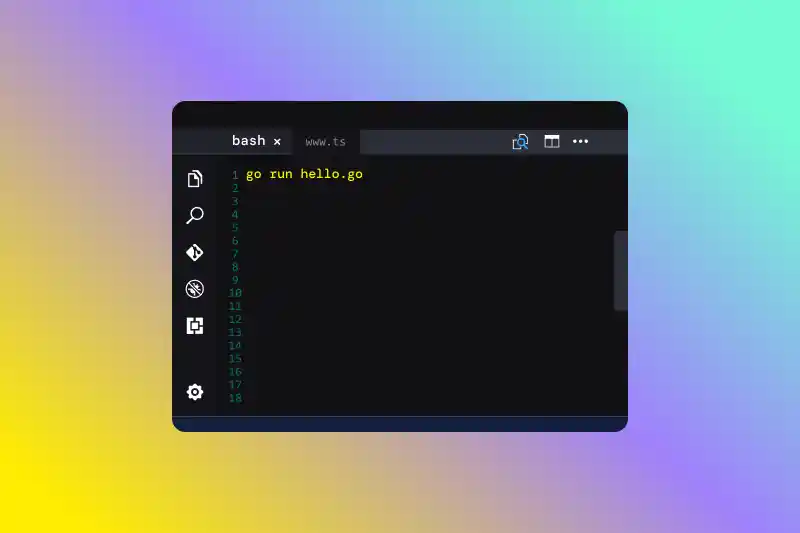
- Run the program:
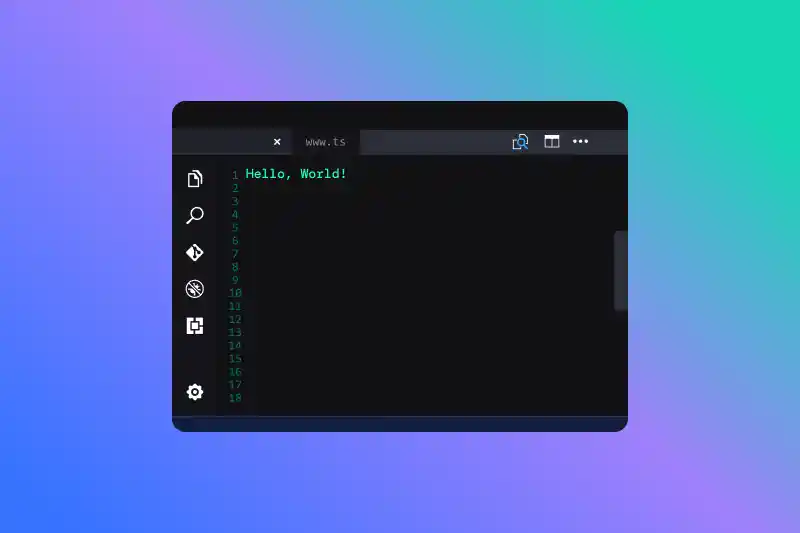
- Output:
8. Conclusion
Above is all the information about what is Golang used for. Golang’s popularity among contemporary programmers is no surprise, as it is widely used for building user-friendly web applications, constructing reliable cloud services, and streamlining DevOps tasks. Mastering variables, functions, and the ability to create effective solutions is essential for leveraging its full potential. Its elegant and efficient coding capabilities make it ideal for modern engineers.
Concurrency is Golang’s bread and butter; the language makes deployment a breeze and is surprisingly low-maintenance. In addition to its technical advantages, Golang features a lively and helpful community. Using it will enhance your skills while also playing a part in the continuous development of the language.